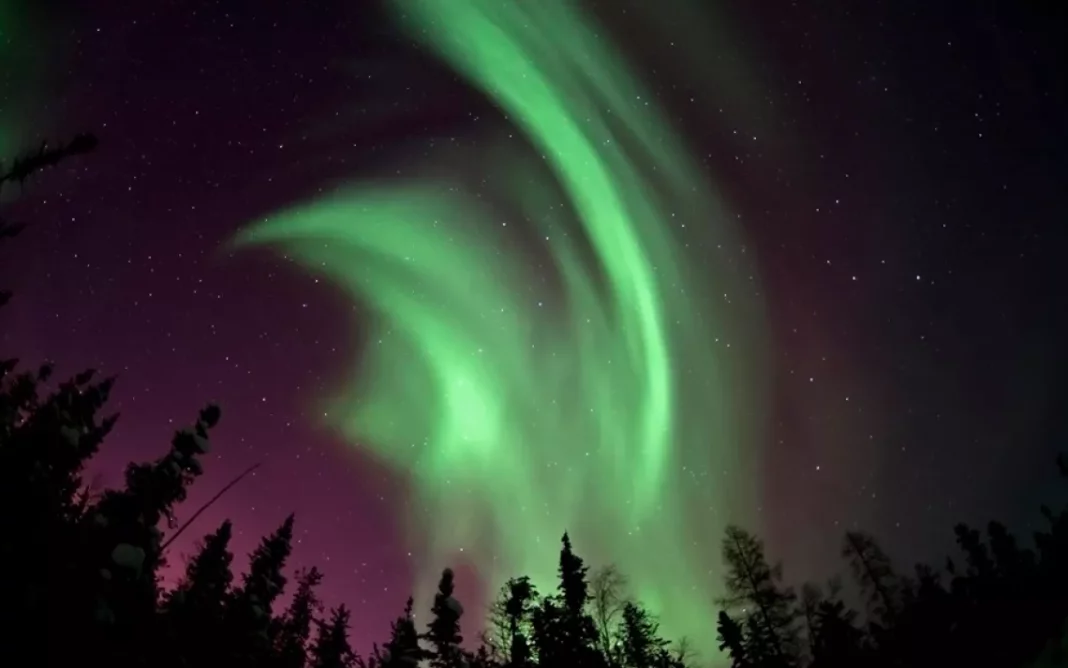
The Aurora Borealis, commonly known as the Northern Lights, is one of nature’s most mesmerizing spectacles. This breathtaking phenomenon lights up the night sky with vibrant colors, ranging from green and pink to red, yellow, and blue. Visible in high-latitude regions, particularly around the Arctic Circle, the Aurora Borealis has fascinated humans for centuries.
The name “Aurora Borealis” combines the name of the Roman goddess of dawn, Aurora, with the Greek word for the north wind, Boreas. This poetic term reflects the mystical and almost otherworldly nature of the lights. Historically, the Aurora Borealis was shrouded in mystery. Ancient cultures often attributed it to supernatural forces or saw it as a message from the gods. The Vikings, for example, believed the lights were reflections of the armor of the Valkyries, while indigenous peoples in North America had their own myths and legends explaining the lights.
Scientifically, the Aurora Borealis is caused by interactions between solar wind and the Earth’s magnetic field. Charged particles from the sun collide with gases in our planet’s atmosphere, producing the stunning light displays. This explanation, however, does not diminish the awe that people feel when witnessing this phenomenon. Instead, it adds to the wonder, showing the incredible natural processes that create such beauty.
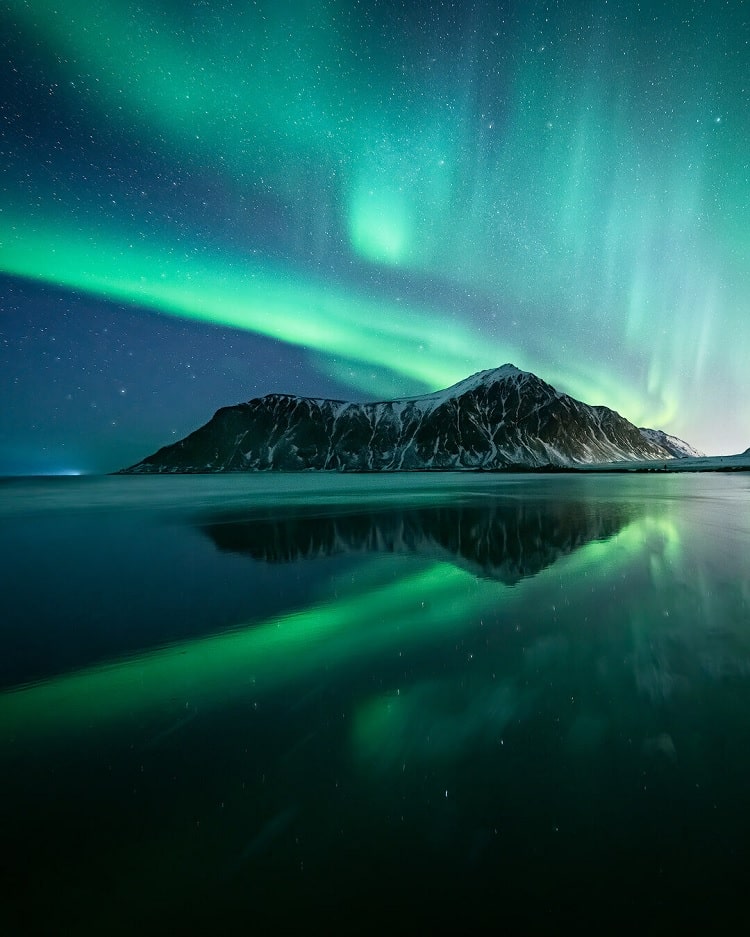

In recent years, advances in technology have made it easier for people to predict and view the Aurora Borealis. Forecasts now allow enthusiasts to plan their trips to see the lights, with the best viewing times typically during the equinoxes in March and September. Popular destinations include Alaska, Norway, Sweden, and Finland, where clear, dark skies provide the perfect backdrop for this light show.
Despite our growing understanding of the Aurora Borealis, it remains a source of wonder and inspiration. Whether you view it as a scientific marvel or a mystical experience, the Northern Lights continue to captivate and enchant, reminding us of the beauty and mystery of our natural world.
The Science Behind the Aurora Borealis: What Causes This Natural Phenomenon?
The Aurora Borealis, often referred to as the Northern Lights, is a captivating natural light display that illuminates the night sky in high-latitude regions. Understanding the science behind the Aurora Borealis adds to its allure, revealing the fascinating processes that produce this spectacular phenomenon.
The story of the Aurora Borealis begins with the sun. The sun continuously emits a stream of charged particles known as the solar wind. When these particles reach Earth, they encounter our planet’s magnetic field, which acts as a protective shield. The Earth’s magnetic field directs the charged particles towards the polar regions, where the field lines converge.
As the solar wind particles collide with the Earth’s atmosphere, they interact with gases such as oxygen and nitrogen. These collisions release energy in the form of light, creating the vivid colors of the Aurora Borealis. The type of gas and altitude of the collision determine the colors observed. Oxygen at higher altitudes (up to 150 miles) produces red and green lights, while nitrogen results in purples and blues.
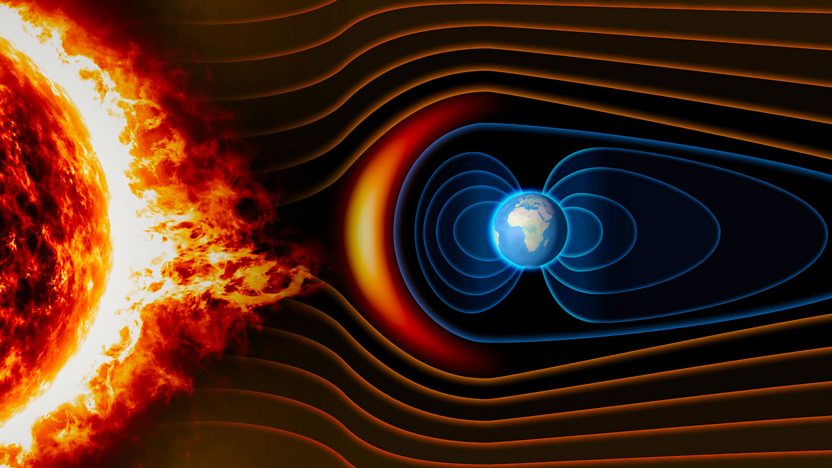
Solar storms, which are large bursts of solar wind and magnetic fields rising above the solar surface, play a significant role in the intensity and frequency of the Aurora Borealis. When a solar storm occurs, it increases the number of charged particles hitting Earth’s atmosphere, leading to more vibrant and widespread auroras. Scientists can now forecast solar storms and predict aurora activity with greater accuracy, allowing aurora enthusiasts to plan their viewing experiences more effectively.
The Earth’s magnetic field, also known as the magnetosphere, is crucial in shaping the Aurora Borealis. It not only directs the charged particles towards the poles but also determines the aurora’s shape and movement. The magnetic field lines guide the particles in a dance across the sky, creating the swirling patterns that make the aurora so mesmerizing.
Research into the Aurora Borealis has expanded our understanding of space weather and its impact on Earth. Scientists continue to study this phenomenon to learn more about the interactions between the solar wind, the Earth’s magnetic field, and our atmosphere. This ongoing research not only unravels the mysteries of the Northern Lights but also helps improve our ability to predict and prepare for solar storms.
In conclusion, the Aurora Borealis is a stunning natural display resulting from the interplay between solar wind, the Earth’s magnetic field, and atmospheric gases. While we now understand the basic science behind this phenomenon, it continues to captivate and inspire, reminding us of the incredible forces at work in our universe.
Aurora Borealis Forecast: When and Where to See the Northern Lights Tonight
The Aurora Borealis, or Northern Lights, is a dazzling display that many people dream of witnessing. Thanks to advancements in technology and forecasting, it’s now easier than ever to predict when and where this stunning phenomenon will be visible. Here’s the latest information to help you catch the Aurora Borealis tonight.
One of the best tools for predicting the Aurora Borealis is the aurora forecast, which provides real-time data on solar wind activity and geomagnetic storms. Websites like the NOAA Space Weather Prediction Center and apps like My Aurora Forecast offer up-to-date predictions on aurora activity. These resources are invaluable for planning your viewing experience.
Tonight, the forecast suggests strong aurora activity due to a recent solar storm. This means the Northern Lights might be visible further south than usual. Typically, the best places to see the Aurora Borealis are within the auroral oval, which includes regions like Alaska, Canada, Scandinavia, and northern Russia. However, under the right conditions, the lights can be seen in unexpected locations.
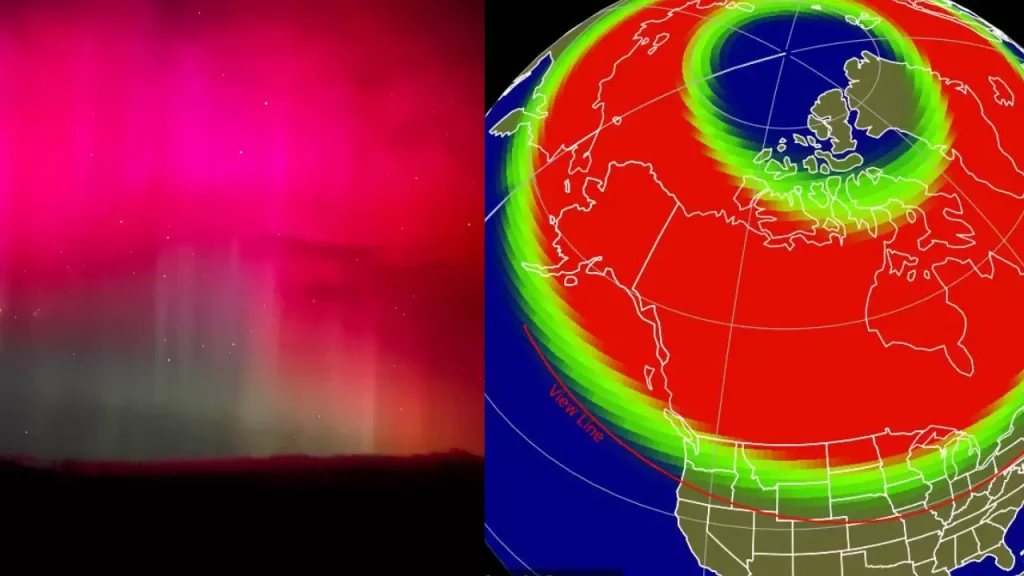
In the United States, Alaska remains the top destination for aurora watching. Cities like Fairbanks and Anchorage offer excellent viewing opportunities, especially during the winter months when the nights are longest and skies are clearest. Tonight, Fairbanks is expected to have a high chance of aurora activity, with clear skies in the forecast.
Surprisingly, the Aurora Borealis might also be visible in parts of the continental United States tonight. In New York, residents in rural areas away from city lights may catch a glimpse of the Northern Lights if the skies remain clear. Similarly, in Chicago, those in less light-polluted suburbs could see the aurora, especially if the solar storm is particularly strong.
For those in southern states like Georgia and Tennessee, aurora sightings are rare but not impossible during significant geomagnetic storms. Keeping an eye on the aurora forecast and finding a dark, open area away from city lights increases your chances of witnessing this natural wonder.
To maximize your chances of seeing the Aurora Borealis tonight, head to a location with minimal light pollution and a clear view of the northern horizon. Dress warmly, bring a blanket or chair, and give your eyes time to adjust to the dark. Patience is key, as the aurora can appear and disappear quickly.
Tonight’s aurora forecast looks promising, especially for those in traditionally favorable locations like Alaska. However, with a bit of luck and preparation, even those in more southern regions might experience the magic of the Aurora Borealis. Keep checking the latest forecasts and head out for a chance to witness one of nature’s most spectacular shows.
Historical Sightings: The Aurora Borealis Through the Ages
The Aurora Borealis, or Northern Lights, has fascinated humans for centuries. Its vibrant, dancing lights have inspired countless legends, myths, and scientific inquiries. Let’s explore the historical sightings of the Aurora Borealis, tracing its journey from ancient times to modern scientific understanding.
Thousands of years ago, people around the world observed the Aurora Borealis and sought to explain its mysterious glow. Ancient civilizations often attributed the lights to supernatural or divine sources. In Norse mythology, the Northern Lights were believed to be reflections from the armor of the Valkyries, warrior maidens who chose those who would die in battle. The Sami people of Scandinavia believed the aurora was the energy of souls, while some Inuit tribes saw it as spirits playing ball with a walrus skull.
The first written record of the Aurora Borealis dates back to 2600 BC in China. Ancient Chinese texts describe “lights of red, yellow, and white” in the northern sky, which aligns with modern descriptions of the aurora. The Roman philosopher Seneca also wrote about a glowing sky in his work “Naturales Quaestiones,” pondering its causes in the 1st century AD.
During the Middle Ages, the Aurora Borealis continued to be a source of wonder and fear. In 1230 AD, the lights were so intense over England that they were documented by monks, who interpreted them as a sign of divine intervention or an omen of great change. Similarly, in 1570 AD, the sky over Europe was illuminated by the aurora, which many saw as a harbinger of the plague.
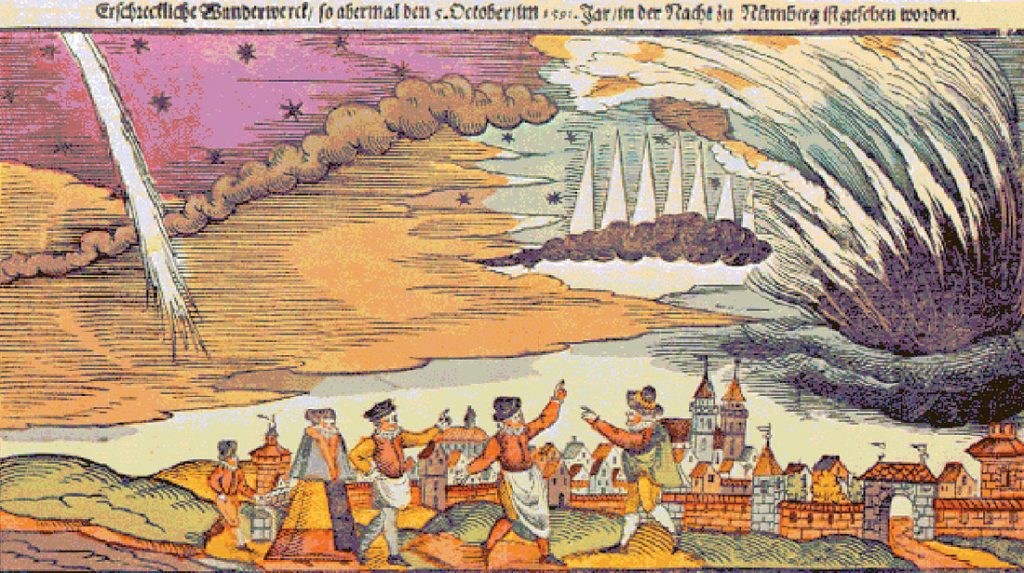

The scientific understanding of the Aurora Borealis began to take shape in the 17th century. In 1621, French astronomer Pierre Gassendi coined the term “Aurora Borealis” after observing the lights over France. He named it after Aurora, the Roman goddess of dawn, and Boreas, the Greek god of the north wind. This marked a shift from mystical interpretations to a more systematic study of the phenomenon.
The 18th and 19th centuries saw significant advances in aurora research. In 1741, British explorer Captain James Cook witnessed the Aurora Borealis during his voyages, bringing back detailed descriptions. By the mid-19th century, scientists began to connect the aurora with solar activity. Norwegian physicist Kristian Birkeland proposed in the early 20th century that the aurora was caused by charged particles from the sun interacting with Earth’s magnetic field, a theory later confirmed with the advent of space exploration.
Today, the Aurora Borealis is understood through the lens of science, yet it remains as captivating as ever. Modern technology allows us to predict and photograph the lights with remarkable accuracy, continuing a tradition of fascination that spans millennia.
The Aurora Borealis has a rich history filled with awe and wonder. From ancient myths to scientific discoveries, the Northern Lights have captivated humanity, illuminating both our skies and our imaginations.
The Aurora Borealis in 2024: What to Expect This Year
The Aurora Borealis, or Northern Lights, promises to be an awe-inspiring spectacle in 2024. As solar activity increases, experts predict a year filled with frequent and vibrant aurora displays. Here’s what you can expect in 2024 regarding aurora sightings, solar storm activity, and the best times and places to view this natural wonder.
Solar activity follows an 11-year cycle, and 2024 is expected to be near the peak of the current cycle, known as the solar maximum. During this period, the sun is more active, producing more solar flares and coronal mass ejections (CMEs). These events release a large number of charged particles into space, some of which interact with Earth’s magnetic field to create the Aurora Borealis. As a result, the increased solar activity in 2024 will likely lead to more frequent and intense auroras.
One of the best ways to predict when the Aurora Borealis will be visible is to monitor solar storm activity. Websites and apps like the NOAA Space Weather Prediction Center and My Aurora Forecast provide real-time updates and predictions. These tools indicate when solar storms are likely to impact Earth, causing aurora displays. In 2024, expect these forecasts to be particularly useful as solar activity ramps up.
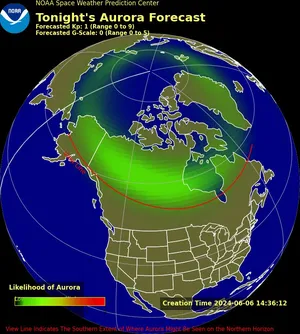
The optimal viewing periods for the Aurora Borealis typically occur around the equinoxes in March and September. During these times, the geomagnetic activity is generally higher, increasing the chances of seeing the Northern Lights. However, with 2024’s heightened solar activity, the auroras may be visible beyond these peak periods, providing more opportunities to witness this stunning display.
For the best aurora viewing experiences, head to high-latitude locations known for clear, dark skies. Alaska remains a top destination, with cities like Fairbanks and Anchorage offering excellent viewing conditions. Scandinavian countries such as Norway, Sweden, and Finland also provide prime spots for aurora watchers. In 2024, these regions are expected to see particularly spectacular displays due to the increased solar activity.
Interestingly, the heightened solar activity might also make the Aurora Borealis visible in regions further south than usual. Places like New York and Chicago could potentially experience aurora sightings, especially during significant solar storms. Keeping an eye on aurora forecasts and heading to areas with minimal light pollution will increase your chances of catching the lights.
In summary, 2024 is shaping up to be an exceptional year for observing the Aurora Borealis. With the solar maximum approaching, we can anticipate more frequent and vibrant displays. By staying informed through reliable aurora forecasts and visiting optimal locations during peak viewing periods, you can maximize your chances of witnessing the breathtaking beauty of the Northern Lights.
Capturing the Magic: Photography Tips for the Aurora Borealis
Photographing the Aurora Borealis, or Northern Lights, can be a magical experience. Capturing this spectacular natural phenomenon requires some knowledge and preparation. Here are practical tips to help you photograph the Aurora Borealis, including camera settings, best practices, and ideal locations.
First, let’s talk about the essential camera settings. For aurora photography, a DSLR or mirrorless camera with manual settings is ideal. Set your camera to manual mode to have full control over the exposure. Start with a wide aperture (f/2.8 or lower) to let in as much light as possible. A low f-number allows your camera to capture the faint light of the auroras more effectively.
Next, adjust your ISO setting. An ISO between 800 and 3200 is a good range to start with. Higher ISO values increase your camera’s sensitivity to light, but be cautious as they can also introduce noise into your images. Experiment with different ISO settings to find the right balance for your camera and conditions.

The shutter speed is another critical factor. To capture the movement of the Aurora Borealis, start with an exposure time of 5 to 30 seconds. Shorter exposures will capture sharper details of the aurora, while longer exposures can create a more fluid, dreamy effect. However, too long an exposure can result in star trails, so adjust accordingly based on the aurora’s activity and brightness.
Using a tripod is essential for stability during long exposures. A remote shutter release or the camera’s built-in timer can help avoid camera shake when taking the shot. Also, consider using manual focus to ensure your images are sharp. Focus on a distant light or a bright star, then switch to manual focus to lock it in place.
Best practices for aurora photography include dressing warmly, as you may spend extended periods outside in cold weather. Bring extra batteries, as cold temperatures can drain them quickly. Scout your location during daylight to find good vantage points and foreground elements like trees, mountains, or bodies of water that can add interest to your composition.
Choosing the right location is crucial. High-latitude regions like Alaska, Norway, Sweden, and Finland offer some of the best opportunities for photographing the Aurora Borealis. These areas provide clear, dark skies away from city lights. Within these regions, places like Fairbanks in Alaska, Tromsø in Norway, and Abisko in Sweden are renowned for their aurora activity and accessible viewing spots.
Photographing the Aurora Borealis requires careful preparation and the right equipment. Use a DSLR or mirrorless camera with manual settings, a wide aperture, a high ISO, and a tripod. Choose a remote location with minimal light pollution, and be prepared for cold conditions. With these tips, you’ll be well-equipped to capture the breathtaking beauty of the Northern Lights.
Planning Your Northern Lights Adventure: Best Locations and Travel Tips
Witnessing the Aurora Borealis, or Northern Lights, is a bucket-list experience for many. Planning a trip to see this spectacular phenomenon requires some preparation. Here’s a guide to help you plan your Northern Lights adventure, including the best locations, optimal times to visit, and essential travel tips.

Best Locations to See the Aurora Borealis
The Aurora Borealis is most commonly observed in high-latitude regions close to the Arctic Circle. Here are some top destinations for your Northern Lights adventure:
- Alaska, USA: Fairbanks is renowned for its aurora activity. The city offers clear skies and numerous tour operators specializing in Northern Lights excursions. Denali National Park is another excellent spot for aurora viewing, providing a stunning natural backdrop.
- Norway: Tromsø, located within the Arctic Circle, is one of the best places to see the Northern Lights. The city is well-equipped for tourists, offering a range of guided tours and activities. The Lofoten Islands and Svalbard are also prime locations for aurora sightings in Norway.
- Sweden: Abisko National Park is a favorite among aurora enthusiasts. The park’s unique microclimate provides clear skies, making it an ideal spot for viewing the lights. Kiruna, the northernmost town in Sweden, is another great base for aurora hunters.
- Finland: Finnish Lapland, particularly the town of Rovaniemi, offers excellent Northern Lights viewing opportunities. The region is also famous for its glass igloos, allowing you to watch the auroras from the comfort of your bed.
- Canada: The Yukon, Northwest Territories, and parts of British Columbia are excellent locations for viewing the Aurora Borealis. Whitehorse and Yellowknife are popular destinations, offering a variety of aurora-focused tours.
Best Times to Visit
The best time to see the Aurora Borealis is during the winter months, from late September to early April. During this period, the nights are long and dark, providing optimal conditions for aurora viewing. The equinoxes in March and September are particularly favorable due to increased geomagnetic activity.
Travel Tips
- Plan Ahead: Book your trip well in advance, especially if you’re traveling during peak aurora season. Accommodations and tours can fill up quickly.
- Check the Forecast: Use aurora forecast websites and apps to monitor solar activity and plan your viewing nights accordingly. Clear, dark skies are essential for the best viewing experience.
- Pack Wisely: Dress in layers to stay warm during long nights outside. Thermal clothing, hats, gloves, and warm boots are a must. Don’t forget essentials like a good camera, tripod, and spare batteries for capturing the lights.
- Stay Flexible: Weather conditions can change rapidly, so be prepared to adjust your plans. Having multiple nights in your itinerary increases your chances of seeing the auroras.
- Explore the Destination: While waiting for the lights, take the opportunity to explore the local culture and enjoy winter activities like dog sledding, snowmobiling, and ice fishing.
For more detailed travel tips, best times to visit, and packing lists, check out our related articles here. With the right planning and a bit of luck, you’ll be well on your way to experiencing the magical Aurora Borealis.
The Enduring Allure of the Aurora Borealis: Join the Global Community of Aurora Hunters
The Aurora Borealis, also known as the Northern Lights, has captured the imagination of people around the world for centuries. This celestial light show, with its shimmering greens, pinks, and purples dancing across the night sky, continues to inspire awe and wonder. From ancient legends to modern scientific discoveries, the Aurora Borealis remains a symbol of nature’s beauty and mystery.
Historically, the Aurora Borealis was surrounded by myths and legends, with various cultures attributing the lights to gods, spirits, or omens. Ancient Chinese records from 2600 BC and Norse mythology both include fascinating interpretations of the aurora. As science advanced, so did our understanding of the phenomenon, leading to significant discoveries in the 17th century and beyond. Today, we know that the Northern Lights are caused by charged particles from the sun interacting with Earth’s magnetic field.
In 2024, the Aurora Borealis is expected to be particularly vibrant due to the peak of the solar cycle. Increased solar activity means more frequent and intense auroras, providing ample opportunities for enthusiasts to witness this natural spectacle. With tools like the NOAA Space Weather Prediction Center and My Aurora Forecast app, predicting and planning for aurora sightings has never been easier.
Capturing the Aurora Borealis on camera requires some preparation. Essential tips include using a DSLR or mirrorless camera with manual settings, a wide aperture, a high ISO, and a tripod. Popular locations for aurora photography include Alaska, Norway, Sweden, and Finland, where the skies are clear and dark, and the auroras are often visible.

Planning a trip to witness the enchanting Aurora Borealis involves choosing the right location and timing. Popular destinations like Alaska, Norway, Sweden, and Finland offer ideal conditions for viewing this celestial spectacle. However, for those seeking a unique adventure beyond the Northern Lights, consider exploring the biodiverse wonders of the Galapagos Islands. These islands, renowned for their endemic species and natural beauty, provide an unforgettable contrast to the Arctic skies. Whether marveling at the auroras or discovering the diverse wildlife of the Galapagos, your journey promises to be a journey of discovery and wonder.
The universal fascination with the Aurora Borealis unites a global community of aurora hunters. Whether you’re an avid photographer, a science enthusiast, or simply someone who appreciates natural beauty, the Northern Lights offer an unforgettable experience. By sharing your experiences and photos, you can inspire others to embark on their own aurora adventures.
Join the global community of aurora hunters and continue exploring the wonders of the Aurora Borealis. Share your stories, connect with fellow enthusiasts, and keep an eye on the skies for the next opportunity to witness one of nature’s most breathtaking displays. The allure of the Aurora Borealis is timeless, and its magic is something that everyone should experience at least once in their lifetime.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What causes the Aurora Borealis?
The Aurora Borealis is caused by solar particles colliding with Earth’s magnetic field, resulting in spectacular light displays.
2. Where is the best place to see the Aurora Borealis?
Prime locations include high-latitude regions near the Arctic Circle, such as Alaska, Norway, and Sweden, known for their clear skies and frequent aurora activity.
3. When is the best time to see the Aurora Borealis?
The optimal viewing times are during winter months, from late September to early April, when nights are long and dark, enhancing visibility of the Northern Lights.
4. How can I photograph the Aurora Borealis?
To capture the Aurora Borealis, use a DSLR camera with manual settings, a wide aperture, and a tripod. Check for dark, clear skies and aim for locations away from city lights.
5. What should I wear to see the Aurora Borealis?
Dress warmly in layers, including thermal clothing, hats, gloves, and insulated boots, to stay comfortable during extended periods outside in cold conditions.
Use of Our Content
⚠️ Content on “Mystery Uncover” is protected under US and International Copyright Laws.
You are free to reuse, republish, and share our content by giving credit to the source as Mystery Uncover with a link to the original material on mysteryuncover.com.






