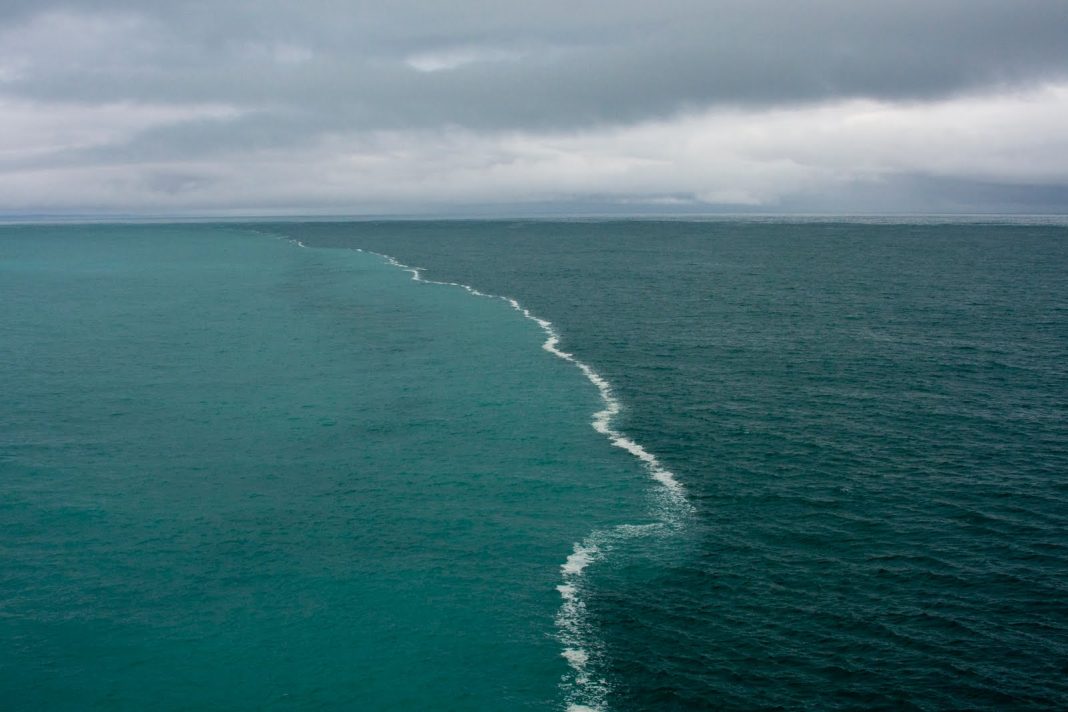
Brackish water is a term you might have heard but not fully understood. Simply put, brackish water is water that has more salt than freshwater but less than seawater. It is often found where freshwater meets the ocean, such as in estuaries, mangroves, and coastal lagoons. This unique type of water plays a crucial role in various ecosystems, supporting a diverse range of plants and animals.
So, what does brackish water mean? The term “brackish” comes from the Middle Dutch word “brak,” meaning salty. Brackish water is characterized by its salinity, which typically ranges from 0.5 to 30 parts per thousand (ppt). For comparison, freshwater has a salinity of less than 0.5 ppt, while seawater usually has a salinity of around 35 ppt. This intermediate level of salinity gives brackish water its distinctive properties.
The definition of brackish water is not just limited to its salinity. It also encompasses the complex and dynamic nature of the environments where it is found. These environments are constantly changing due to the mixing of freshwater and seawater, creating unique conditions that can support specialized species of fish, plants, and other organisms.
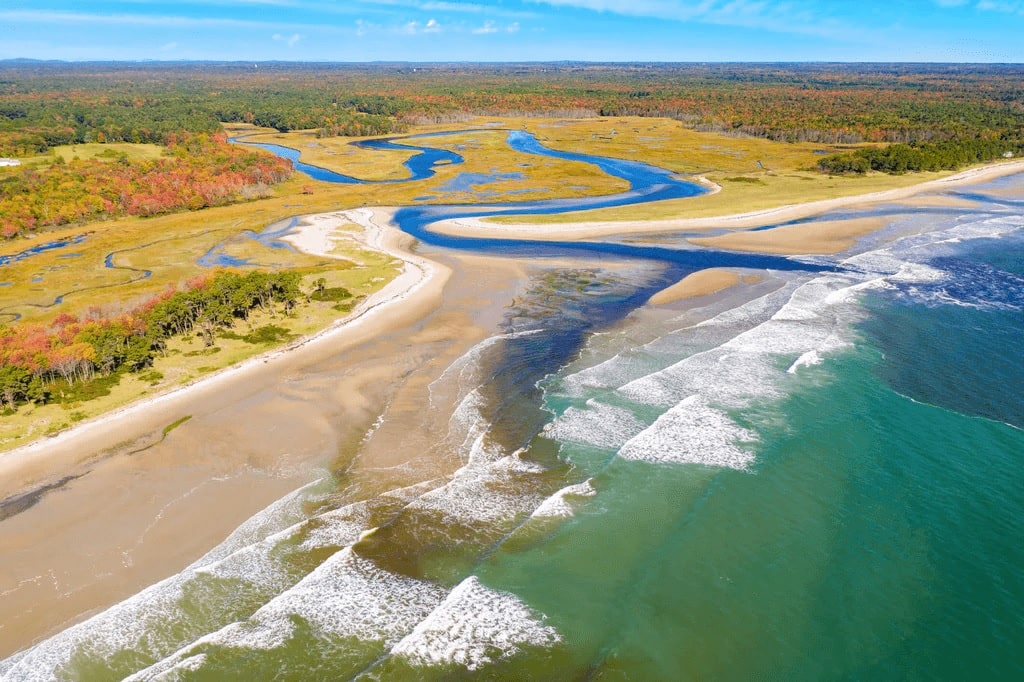

Brackish water environments are vital for many reasons. They serve as nurseries for various fish species, providing a safe haven for young fish to grow and develop before heading out to the open sea. Additionally, they act as natural filters, helping to remove pollutants from the water and improve overall water quality. The plants found in these areas, such as mangroves and seagrasses, play a crucial role in stabilizing shorelines and preventing erosion.
Understanding brackish water is essential for environmental conservation efforts. As human activities and climate change continue to impact these delicate ecosystems, it is more important than ever to recognize their value and work towards their preservation. By learning about brackish water and its significance, we can better appreciate the delicate balance of our natural world and the need to protect it for future generations.
The Formation of Brackish Water: Natural Occurrences and Human Influence
Brackish water forms in various natural settings and is also influenced by human activities. Understanding where brackish water is found and the factors that contribute to its formation can help us appreciate its significance and the delicate balance of its ecosystems.
Naturally, brackish water is found in areas where freshwater mixes with seawater. This typically occurs in estuaries, which are bodies of water where rivers meet the sea. Estuaries are among the most productive ecosystems on Earth, supporting a wide variety of plant and animal life. Mangroves, which are coastal forests found in tropical and subtropical regions, also contain brackish water. These unique trees thrive in the mix of freshwater and saltwater, providing habitat for many species. Coastal lagoons and marshes are other common locations where brackish water can be found. These areas often have a fluctuating salinity level due to tidal movements and freshwater inflow from rivers or rainfall.
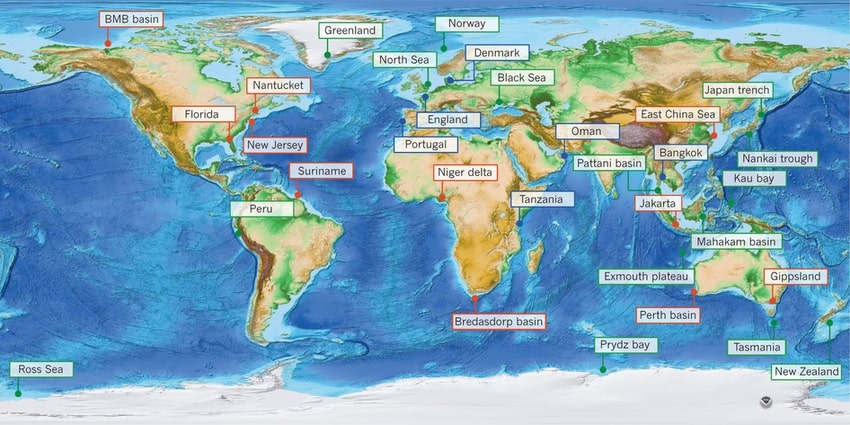
The salinity of brackish water can vary greatly depending on several factors. For instance, in an estuary, the salinity might be higher near the ocean and lower further upstream where the freshwater input is stronger. This variation in salinity creates a range of habitats within a single ecosystem, each supporting different types of organisms adapted to specific salinity levels.
Human activities can significantly influence the formation and salinity of brackish water. One major factor is freshwater diversion for agriculture and urban use, which can reduce the amount of freshwater flowing into estuaries and increase their salinity. Conversely, excessive freshwater runoff from storms, agricultural irrigation, or dam releases can decrease the salinity, impacting the organisms adapted to brackish conditions. Pollution from industrial discharge and agricultural runoff can also affect the quality and salinity of brackish water, harming the ecosystems that depend on it.
To understand how brackish your water is, you can measure its salinity using a hydrometer or a refractometer. These tools can give you a precise reading of the salt concentration in the water, helping you determine if it falls within the brackish range. Knowing the salinity of your water is crucial for maintaining healthy brackish water aquariums and for the conservation of natural brackish water habitats.
The formation of brackish water is a dynamic process influenced by both natural occurrences and human activities. Recognizing where brackish water is found and understanding the factors that affect its salinity are essential steps in preserving these vital ecosystems for future generations.
Characteristics and Salinity of Brackish Water
Brackish water is unique due to its intermediate salinity, which falls between that of freshwater and seawater. Understanding the characteristics and salinity of brackish water is essential for comprehending its ecological importance and the adaptations of organisms that live in these environments.
The salinity of brackish water typically ranges from 0.5 to 30 parts per thousand (ppt). To put this in perspective, freshwater has a salinity of less than 0.5 ppt, while seawater usually has a salinity of around 35 ppt. The amount of salt in brackish water varies depending on the specific location and the mixing of freshwater and seawater. For example, in an estuary where a river meets the sea, the salinity can change dramatically from one spot to another. Near the mouth of the river, the water may be fresher, while closer to the open ocean, the salinity increases.
The dynamic nature of brackish water environments means that the salinity can also fluctuate over time. Tides play a significant role in this variation. During high tide, seawater pushes further into estuaries and lagoons, raising the salinity. Conversely, during low tide, the influence of freshwater increases, reducing the salinity. Seasonal changes, such as heavy rainfall or drought, can also impact the salinity levels of brackish water.
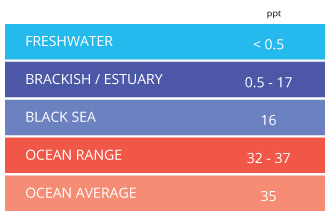
The unique salinity of brackish water creates specific conditions that influence the types of plants and animals that can thrive in these environments. Many species have adapted to the fluctuating salinity levels. For instance, certain types of fish, like the brackish water pufferfish and some species of mollies, are well-suited to these conditions. Mangrove trees, which are commonly found in brackish water areas, have specialized roots that filter out salt, allowing them to survive in high-salinity environments.
Measuring the salinity of brackish water is crucial for various applications, including maintaining aquariums and monitoring environmental health. Tools like hydrometers and refractometers are commonly used to measure the salt concentration in water. These instruments provide accurate readings that help in determining the suitability of water for different species and ensuring the stability of brackish water habitats.
The salinity of brackish water is a defining characteristic that influences the ecosystems where it is found. By understanding how much salt is in brackish water and the factors that affect its salinity, we can better appreciate the complex interactions within these unique environments and the importance of preserving them.
Brackish Water Ecosystems: Plants, Fish, and Animals
Brackish water ecosystems are unique environments where freshwater meets seawater, creating a habitat with intermediate salinity. These ecosystems support a diverse range of plants, fish, and animals that have adapted to the fluctuating conditions of brackish water.
One of the most notable features of brackish water ecosystems is their plant life. Mangroves are iconic plants found in these areas, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions. These trees have specialized roots that can filter out salt, allowing them to thrive in saline conditions. Mangrove forests provide critical habitat for numerous species, offering shelter and breeding grounds. Other plants found in brackish water include seagrasses and salt-tolerant reeds, which contribute to the stability and productivity of these ecosystems.
The fish species that inhabit brackish water are uniquely adapted to its varying salinity levels. Some common examples of brackish water fish include the green spotted pufferfish, which is known for its distinctive coloration and the ability to tolerate a wide range of salinities. Another example is the molly fish, which can thrive in both freshwater and brackish water environments. Gobies, which are small, bottom-dwelling fish, are also frequently found in brackish water habitats. These fish often exhibit behaviors and physiological adaptations that enable them to survive in fluctuating salinity.
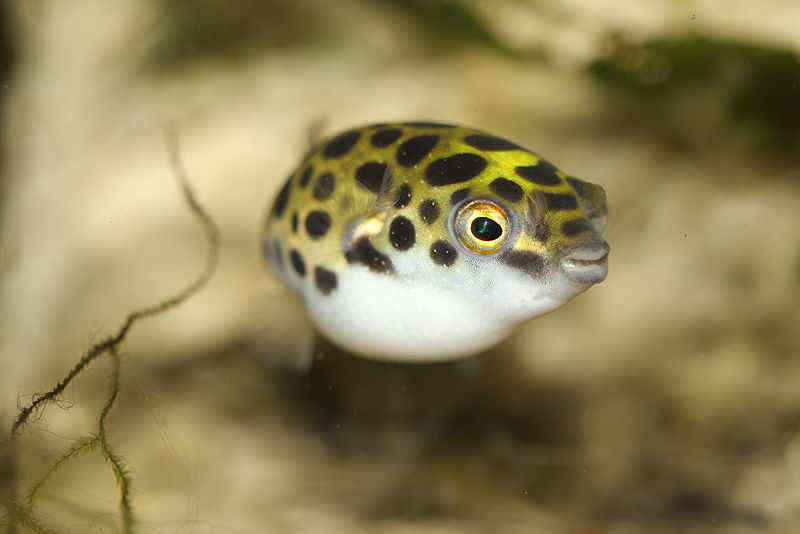

In addition to fish, brackish water ecosystems are home to a variety of other animals. Crustaceans such as fiddler crabs and red claw crabs are commonly found in these areas. These crabs play an essential role in the ecosystem by burrowing in the mud, which helps to aerate the soil and facilitate nutrient cycling. Brackish water is also home to certain species of shrimp, which are important both ecologically and economically. Birds, including herons and egrets, often frequent brackish water environments to feed on the abundant fish and invertebrates.
Understanding the complexity of brackish water ecosystems is crucial for their conservation. These habitats are often threatened by human activities such as pollution, coastal development, and freshwater diversion. Protecting brackish water environments requires efforts to maintain the delicate balance of salinity and ensure the health of the diverse species that depend on these unique habitats.
Brackish water ecosystems are rich in biodiversity, supporting a variety of plants, fish, and animals adapted to intermediate salinity conditions. From mangroves and seagrasses to pufferfish and crabs, these ecosystems play a vital role in the environment and require our attention and conservation efforts to thrive.
Creating and Maintaining a Brackish Water Aquarium
Setting up a brackish water aquarium can be a rewarding experience, providing a unique environment for a variety of fascinating fish and aquatic creatures. Understanding how to make brackish water and properly maintain it is essential for the health and well-being of your aquarium inhabitants.
To create brackish water, you need to start with freshwater and gradually add marine salt until you achieve the desired salinity. The salinity of brackish water typically ranges from 0.5 to 30 parts per thousand (ppt). For a brackish water aquarium, a common target is around 1.005 to 1.015 specific gravity, which can be measured using a hydrometer or refractometer. It is crucial to add the marine salt slowly and allow it to dissolve completely before testing the water’s salinity.
Setting up a brackish water aquarium involves several key steps. First, choose an appropriately sized tank for the species you plan to keep. Brackish water fish and invertebrates often require ample space to thrive. Next, install a good filtration system to maintain water quality, as brackish water can be more challenging to keep clean compared to freshwater. Use a substrate suitable for brackish water, such as sand or gravel, and add decorations like rocks and driftwood that can provide hiding places and enrichment for your aquarium inhabitants.
When creating a brackish water environment for specific species, such as red claw crabs and fiddler crabs, it’s important to cater to their unique needs. These crabs require both land and water areas in the tank. You can create a land area using a platform or by sloping the substrate to allow the crabs to climb out of the water. Ensure that the water’s salinity is appropriate for the species, typically around 1.005 to 1.010 specific gravity. Regularly monitor the water parameters to keep the environment stable and healthy.
Choosing the right fish for your brackish water aquarium is also vital. Some popular brackish water fish include mollies, which are adaptable and easy to care for, and the green spotted pufferfish, known for its distinctive appearance and playful behavior. Other suitable fish are knight gobies and scats, both of which can thrive in the unique conditions of a brackish water tank.

Maintaining a brackish water aquarium requires regular monitoring of water quality and salinity. Perform water changes as needed, using brackish water mixed to the same salinity as the tank. Keeping the tank clean and the water parameters stable will ensure the health and happiness of your aquarium inhabitants.
Creating and maintaining a brackish water aquarium involves understanding how to make brackish water, setting up the tank properly, and choosing suitable species. With careful planning and regular maintenance, you can enjoy the beauty and diversity of a thriving brackish water ecosystem in your own home.
Uses and Applications of Brackish Water
Brackish water, with its unique mix of salt and freshwater, serves various purposes in different industries and environmental settings. While it is not suitable for drinking, advancements in technology have made it possible to utilize brackish water in several beneficial ways.
One of the most frequently asked questions is, “Can you drink brackish water?” The short answer is no. Brackish water contains higher levels of salt than freshwater, making it unsuitable for direct consumption. Drinking brackish water can lead to dehydration and other health issues because the body requires more water to expel the excess salt. However, with the increasing scarcity of freshwater resources, scientists and engineers have developed methods to make brackish water safe for drinking.
A key method used to treat brackish water is reverse osmosis. Brackish water reverse osmosis is a process that involves pushing water through a semi-permeable membrane to remove salts and other impurities. This method is highly effective and has been adopted in various parts of the world to provide potable water. Reverse osmosis systems are capable of treating brackish water with salinity levels of up to 10,000 parts per million (ppm). The result is clean, drinkable water that meets health and safety standards.
In addition to providing potable water, brackish water is used in agriculture and aquaculture. In areas where freshwater is scarce, brackish water can be utilized for irrigation, provided that the salinity levels are managed to prevent soil degradation. Certain crops, such as salt-tolerant varieties of tomatoes and barley, can be cultivated using brackish water. This practice helps conserve freshwater resources and supports sustainable agriculture.
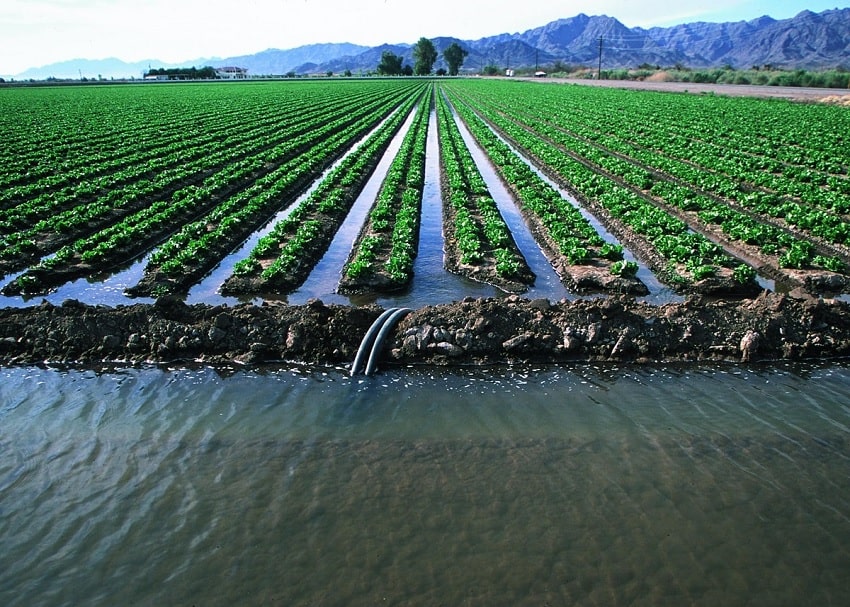

Brackish water is also vital in aquaculture, where it is used to raise fish and other aquatic organisms. Species such as tilapia, shrimp, and certain types of crabs thrive in brackish water conditions. Aquaculture farms often use brackish water to mimic the natural habitats of these species, promoting healthy growth and reducing the strain on freshwater supplies.
Furthermore, brackish water plays a role in industrial processes. Many industries, including power generation and mining, require large volumes of water for cooling and other operations. Brackish water is often used as an alternative to freshwater, helping to reduce the demand on limited freshwater resources.
While you cannot drink brackish water directly, its uses and applications are extensive and varied. Through processes like reverse osmosis, brackish water can be transformed into a valuable resource for drinking, agriculture, aquaculture, and industry. These applications highlight the importance of brackish water in addressing global water challenges and promoting sustainable resource management.
The Future of Brackish Water: Environmental and Scientific Perspectives
The future of brackish water is a topic of significant interest to environmentalists and scientists alike. As our understanding of these unique ecosystems grows, modern research and ongoing studies are shedding light on their importance and the challenges they face, particularly in the context of climate change.
Modern research into brackish water environments has highlighted their crucial role in biodiversity and ecosystem health. These areas, where freshwater meets seawater, are rich in nutrients and provide habitat for a diverse array of species. Scientists are studying the complex interactions within these ecosystems to better understand how they function and how they can be protected. For example, research has shown that mangrove forests, which thrive in brackish water, act as carbon sinks, sequestering large amounts of carbon dioxide and helping to mitigate climate change. Additionally, studies are examining how brackish water fish and plants have adapted to fluctuating salinity levels, offering insights into the resilience of these species.
Ongoing studies are also exploring the potential of brackish water for sustainable aquaculture and agriculture. By cultivating salt-tolerant crops and aquaculture species in brackish water, researchers hope to alleviate pressure on freshwater resources and promote food security. Innovations in brackish water usage could lead to more sustainable farming practices, particularly in arid regions where freshwater is scarce.
The impact of climate change on brackish water environments is a growing concern. Rising sea levels, increased temperatures, and altered precipitation patterns are all affecting the delicate balance of salinity in these ecosystems. For instance, higher sea levels can push saltwater further inland, increasing the salinity of brackish water areas and potentially harming freshwater species that are not adapted to such conditions. Conversely, more intense rainfall can dilute salinity levels, impacting species that require higher salinity to thrive.
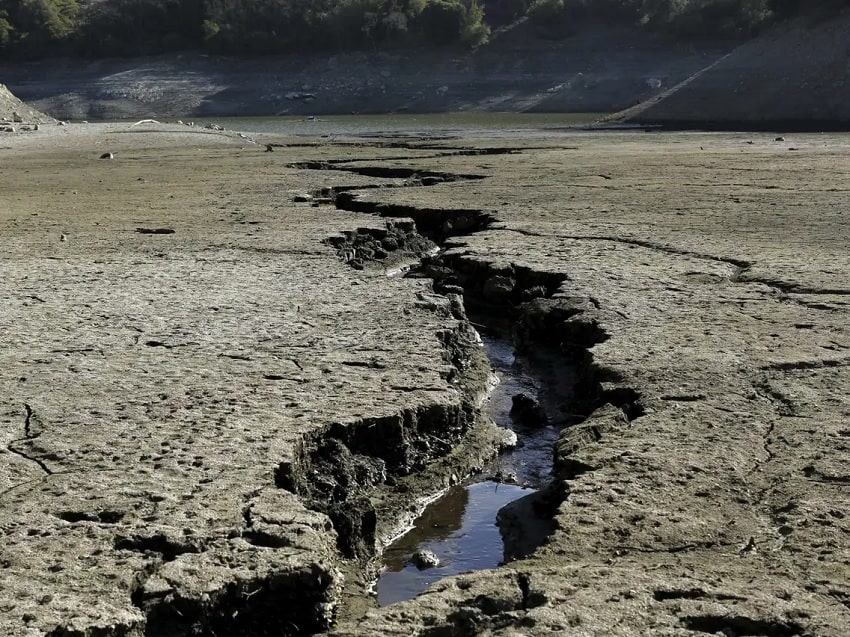

Climate change also poses a threat to the structural integrity of brackish water habitats. Mangroves and coastal marshes, which rely on a stable mix of freshwater and saltwater, are particularly vulnerable. Erosion, increased storm surges, and human activities such as coastal development further exacerbate the risks. Protecting and restoring these habitats is essential for maintaining the biodiversity and ecological services they provide.
In response to these challenges, scientists and conservationists are advocating for the implementation of adaptive management strategies. These strategies include monitoring salinity levels, restoring degraded habitats, and promoting policies that reduce greenhouse gas emissions. By enhancing our understanding of brackish water ecosystems and their response to environmental changes, we can develop more effective conservation measures.
In conclusion, the future of brackish water depends on our ability to adapt to and mitigate the impacts of climate change. Modern research and ongoing studies are crucial for uncovering the complexities of these ecosystems and finding sustainable ways to protect and utilize them. As we face an uncertain environmental future, the importance of preserving brackish water environments cannot be overstated.
At Mystery Uncover, we delve into the intriguing stories and scientific mysteries of the world’s most fascinating phenomena. From the depths of the ocean to the far reaches of space, our articles provide in-depth insights and uncover the hidden truths behind the mysteries that captivate us all. To learn more about other fascinating water bodies, you might be interested in exploring Why is it Called the Dead Sea?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is brackish water?
Brackish water is water that has more salinity than freshwater but not as much as seawater. It typically has a salinity range of 0.5 to 30 parts per thousand (ppt), making it suitable for certain species of fish and plants adapted to these conditions.
2. How do you create brackish water for an aquarium?
To create brackish water for an aquarium, start with freshwater and gradually add marine salt until you achieve the desired salinity, typically around 1.005 to 1.015 specific gravity. It’s essential to use a hydrometer or refractometer to monitor and maintain the salinity level suitable for your aquarium inhabitants.
3. Can you drink brackish water?
No, brackish water is not suitable for drinking due to its higher salt content compared to freshwater. Drinking brackish water can lead to dehydration and health issues, as the body requires more water to expel the excess salt.
4. What fish and plants thrive in brackish water?
Several species of fish thrive in brackish water, including mollies, pufferfish, gobies, and certain types of crabs. Likewise, plants such as mangroves, salt marsh grasses, and certain algae species are adapted to brackish water conditions.
5. How does climate change affect brackish water ecosystems?
Climate change poses significant threats to brackish water ecosystems by altering salinity levels, increasing sea levels, and disrupting habitat conditions. These changes impact the biodiversity and ecological balance of brackish water environments, necessitating conservation efforts.
Use of Our Content
⚠️ Content on “Mystery Uncover” is protected under US and International Copyright Laws.
You are free to reuse, republish, and share our content by giving credit to the source as Mystery Uncover with a link to the original material on mysteryuncover.com.






