In the annals of scientific history, few instruments embody the fusion of art, science, and spirituality as eloquently as the astrolabe. This intricate device, often described as the “laptop of the medieval world,” has captivated scholars and astronomers for centuries, particularly within the Islamic Golden Age.
The history and significance of astrolabes in Islamic culture offer a fascinating glimpse into a period where science and religion coexisted harmoniously, driving innovations that would influence both the Islamic world and later European science. Understanding the role of the astrolabe within this cultural and intellectual framework reveals not only the technical advancements of the era but also the profound cultural exchanges that shaped the medieval world.

What We Know: The Origins and Functionality of the Astrolabe
The astrolabe, though reaching its zenith in the Islamic world, has its origins in ancient Greece. The device was refined and adapted by Islamic scholars, who expanded its use far beyond the simple astronomical observations for which it was initially designed. The fact that the astrolabe was developed in the Muslim empire implies a deep-seated reverence for knowledge, both scientific and spiritual, that characterized Islamic culture during the medieval period.
An astrolabe is a complex instrument with multiple components—primarily a disk called the mater, a rotating plate known as the rete, and several other parts, including the alidade, used for sighting objects. Its primary function was to solve problems related to time and the position of celestial bodies, aiding in tasks such as determining prayer times, finding the Qibla (direction of Mecca), and navigating by the stars. The versatility of the astrolabe made it an essential tool for scholars and travelers alike.
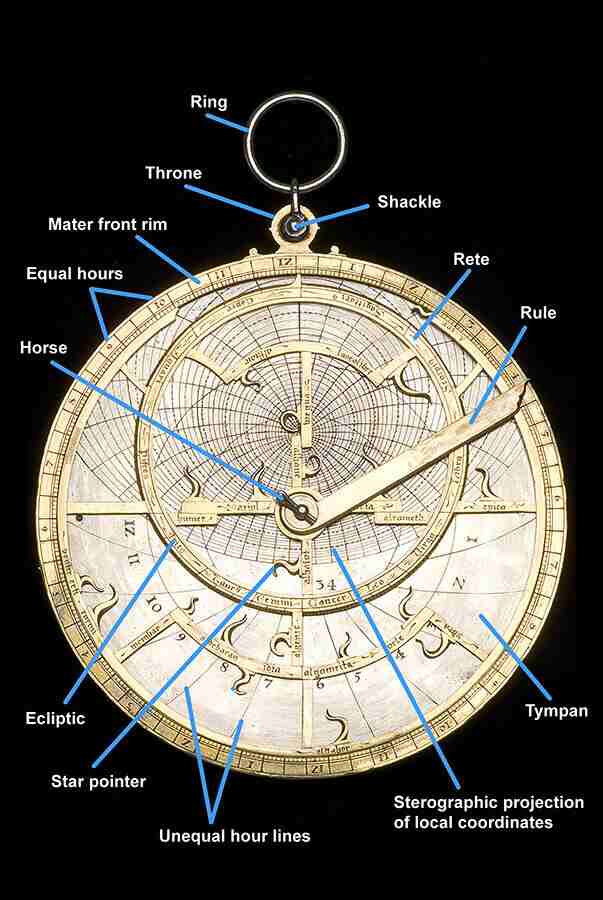
Islamic scientists, such as Al-Farghani, Al-Battani, and Al-Zarqali, were instrumental in advancing the design and functionality of the astrolabe. They added innovations that allowed for the calculation of the height of objects, measurement of the depth of wells, and even complex trigonometric calculations. These advancements underscore the astrolabe’s role as not merely a scientific tool but as a symbol of the broader Islamic contributions to astronomy and mathematics.
Mysteries Surrounding Astrolabes
Despite the wealth of knowledge we possess about astrolabes, certain aspects of their history remain shrouded in mystery. For instance, while it is widely accepted that the astrolabe was introduced to Europe through Islamic Spain, the precise timeline and the extent of its influence on European scientific thought are still debated.
Moreover, the methods by which Islamic scholars developed and standardized astrolabe designs across such a vast empire, stretching from Spain to India, are not fully understood. This standardization speaks to a highly sophisticated network of communication and knowledge transfer that has yet to be fully explored. For further insights into how these cultural exchanges shaped medieval science, consider reading about the Baghdad Battery’s significance.
Another unresolved question is the origin of specific design elements in Islamic astrolabes, which often include intricate geometric patterns and inscriptions. These designs are not merely decorative; they carry symbolic meanings that intertwine with the Islamic understanding of the cosmos. The full extent to which these designs influenced European artistic and scientific endeavors is a topic that warrants further research, especially considering the cultural exchanges between Islamic and European scholars during the Middle Ages.
Furthermore, while the practical uses of the astrolabe in navigation and timekeeping are well-documented, its role in the more esoteric aspects of Islamic spirituality, such as astrology and alchemy, remains less clear. The intersection of science and mysticism in Islamic culture often defies the modern separation of these fields, leading to intriguing, yet unanswered, questions about the broader uses of the astrolabe.

Theories and Speculation: The Astrolabe’s Influence and Legacy
Several theories have emerged to explain the far-reaching impact of the astrolabe on both Islamic and European cultures. One prominent theory suggests that the astrolabe’s design and use in the Islamic world laid the groundwork for later European advancements in astronomy and navigation.
This theory is supported by historical records showing that many of the earliest European astrolabes were directly inspired by Islamic models, with scholars like Regiomontanus and Copernicus drawing on Islamic astronomical texts to develop their own theories. For a comprehensive overview of the history of the astrolabe, including its development and use in various cultures, visit this detailed resource.
Another area of speculation involves the astrolabe’s role in facilitating cultural exchange between Islamic and European scientists. The astrolabe’s diffusion throughout Europe, particularly through Spain, serves as a tangible example of the broader intellectual exchanges that took place during the Middle Ages. Some historians argue that the astrolabe was a key instrument in the transmission of not just scientific knowledge, but also philosophical and theological ideas that would later underpin the Renaissance.
There is also ongoing debate about the extent to which the astrolabe influenced other scientific instruments, such as the armillary sphere and the quadrant. While the astrolabe is often seen as a precursor to these devices, the exact nature of this relationship is still unclear. Some scholars suggest that the astrolabe’s influence on the development of the armillary sphere, for example, was more symbolic than practical, serving as a conceptual model rather than a direct technological predecessor.
Moreover, the astrolabe’s influence extended beyond the realm of science into the decorative arts. The intricate designs found on many Islamic astrolabes likely influenced European art, particularly in the realms of geometry and architectural design. This artistic exchange, though less studied, highlights the astrolabe’s multifaceted legacy.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What was the astrolabe used for?
The astrolabe was primarily used for astronomical observations, determining prayer times, finding the Qibla, and navigating by the stars.
2. Can an astrolabe help you find the Qibla?
Yes, one of the astrolabe’s key functions in the Islamic world was to determine the direction of the Qibla, or the direction of Mecca, for prayer.
3. What did the Muslims use the astrolabe and the armillary sphere for?
Muslims used the astrolabe for timekeeping, navigation, and determining celestial positions, while the armillary sphere was primarily used for teaching and illustrating the celestial sphere’s movement.
4. What is the full meaning of astrolabe?
The term “astrolabe” comes from the Greek words “astron,” meaning star, and “lambanein,” meaning to take or to measure. It literally means “star-taker.”
5. How did the invention of the astrolabe help Vasco da Gama make his voyage to India?
The astrolabe, by enabling more precise navigation, allowed explorers like Vasco da Gama to chart more accurate courses, facilitating longer ocean voyages, such as his journey to India.
The Astrolabe – A Testament to Islamic Scientific Prowess
The history and significance of astrolabes in Islamic culture cannot be overstated. These instruments are not just relics of a bygone era but symbols of a civilization that valued knowledge, innovation, and the harmonious blending of science and spirituality. The unanswered questions surrounding the astrolabe—its exact origins, its full range of uses, and its influence on later scientific developments—serve as a reminder of the complexities of history and the ongoing quest to uncover the truths of our past.
As we continue to explore these mysteries, the astrolabe stands as a testament to the scientific advancements in Islamic culture and its profound influence on the world. While many aspects of its history remain to be fully understood, the legacy of the astrolabe in both Islamic and European contexts is a powerful example of how knowledge transcends borders, shaping civilizations across time and space.
Use of Our Content
⚠️ Content on “Mystery Uncover” is protected under US and International Copyright Laws.
You are free to reuse, republish, and share our content by giving credit to the source as Mystery Uncover with a link to the original material on mysteryuncover.com.





