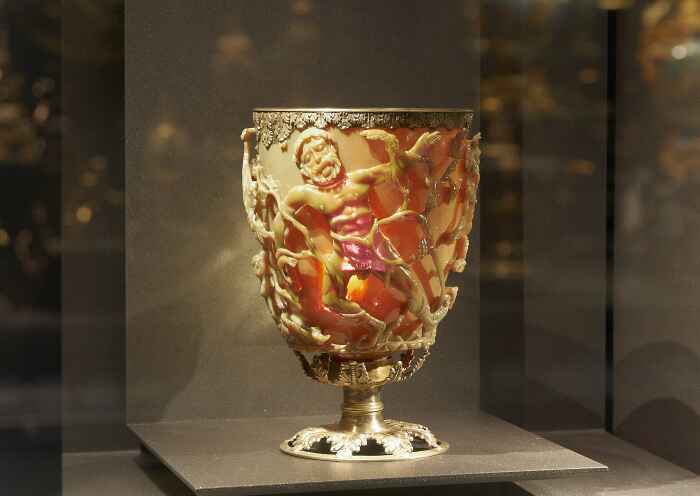
The Lycurgus Cup, a captivating artifact from ancient Rome, stands as a testament to the advanced craftsmanship and technological prowess of its creators. This mysterious goblet, which changes color under different lighting conditions, has intrigued scientists and historians alike for centuries. In this article, we will delve into the history, significance, and technological marvels of the Lycurgus Cup, exploring its journey from antiquity to the modern era.
The Discovery and Historical Context
The Lycurgus Cup, an enigmatic relic from ancient Rome, emerged from the shadows of history in the 19th century. Its discovery added a new chapter to our understanding of Roman craftsmanship and technological prowess. While the exact circumstances and location of its unearthing remain shrouded in mystery, the cup quickly captivated the imagination of scholars and art enthusiasts alike.
Believed to have been crafted in the 4th century AD, the Lycurgus Cup features a depiction of King Lycurgus, a figure from Greek mythology, entangled in vines. This scene symbolizes his punishment by Dionysus, the god of wine, for attempting to suppress his worship. This intricate narrative not only highlights the Romans’ artistic skills but also reflects their fascination with mythological themes.
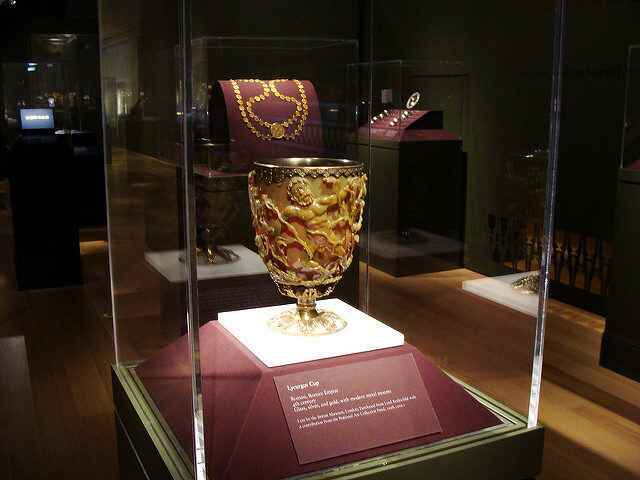

Upon its discovery, the Lycurgus Cup was recognized as a significant artifact from late antiquity. Early analyses focused on its artistic value and the mythological story it portrayed. Art historians marveled at the detailed craftsmanship and the vivid imagery that brought ancient myths to life. The cup’s initial reception was primarily within the realms of art and mythology, with little attention given to its more mysterious properties.
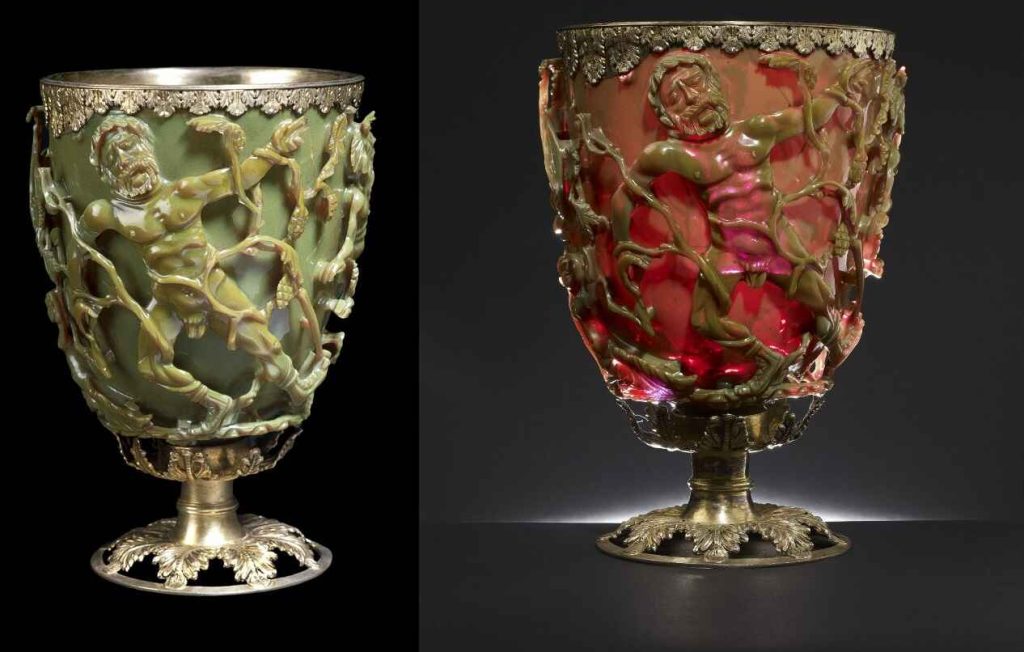
As the 19th century progressed, scientific curiosity began to grow. Researchers noticed the cup’s unique ability to change color depending on the light source, a phenomenon that defied simple explanation. In natural light, the cup appeared to be a translucent green, while in backlit conditions, it transformed into a deep, rich red. This dichroic effect sparked intrigue and led to further investigation.
It wasn’t until the 20th century that advancements in technology allowed scientists to delve deeper into the secrets of the Lycurgus Cup. Through the use of electron microscopy and other analytical techniques, researchers discovered that the color-changing property was due to the presence of nanoparticles of gold and silver embedded within the glass. These particles, incredibly small and uniformly dispersed, interact with light in such a way that they produce different colors under varying lighting conditions.
This discovery was groundbreaking, as it revealed that the Romans had developed an early form of nanotechnology, centuries before the term was coined. The realization that ancient craftsmen possessed such advanced knowledge and skills challenged previously held assumptions about technological progress and innovation.
The historical context of the Lycurgus Cup places it in a period of Roman history marked by artistic and scientific achievements. During the 4th century AD, the Roman Empire was experiencing both cultural flourishing and political turbulence. This duality is reflected in the cup itself: a masterpiece of artistic expression and a marvel of technological ingenuity.
The Craftsmanship and Technology Behind the Lycurgus Cup
The Lycurgus Cup, beyond its captivating mythological depiction, stands as a remarkable example of ancient craftsmanship and early technological innovation. To understand how this extraordinary artifact was created, we must journey back to the workshops of 4th century AD Rome, where skilled artisans worked with glass in ways that still astonish us today.
The Art of Glassmaking in Ancient Rome
Roman glassmaking had already reached an advanced stage by the time the Lycurgus Cup was created. Glassmakers employed sophisticated techniques, combining different materials and processes to achieve a variety of colors and effects. The creation of the Lycurgus Cup, however, required a mastery that went beyond conventional glassmaking.
How Was the Lycurgus Cup Made?
The Lycurgus Cup is made of dichroic glass, a material that exhibits two different colors when viewed from different angles. This effect is due to the presence of nanoparticles of gold and silver, suspended within the glass matrix. The precise method of incorporating these particles into the glass is still not entirely understood, but modern analysis suggests a process of extreme care and precision.

First, the glass was blown and shaped into the desired form. The intricate carving, depicting the story of King Lycurgus, was then meticulously executed. This level of detail required not only artistic talent but also technical expertise. The artisans likely used a combination of tools to carve the glass, ensuring that the imagery was both clear and durable.
The Nanotechnology of the Lycurgus Cup
The real marvel of the Lycurgus Cup lies in its use of nanotechnology. The Romans achieved the dichroic effect by embedding particles of gold and silver, each only about 70 nanometers in diameter, into the glass. To put this into perspective, a nanometer is one-billionth of a meter, highlighting the incredible precision required.
These nanoparticles scatter light in specific ways, causing the glass to appear green when lit from the front and red when lit from behind. This phenomenon, known as plasmon resonance, was harnessed by the Roman craftsmen, albeit without the modern scientific understanding we have today. Their empirical knowledge, developed through centuries of trial and error, allowed them to manipulate materials at a microscopic level.
The Legacy of Roman Nanotechnology
The discovery of these techniques has revolutionized our understanding of ancient technology. The Lycurgus Cup is not just a piece of art; it is a testament to the advanced knowledge possessed by Roman artisans. It challenges the notion that technological progress is a linear path, showing that remarkable innovations can arise in seemingly unexpected places and times.
In studying the craftsmanship and technology behind the Lycurgus Cup, we gain insights into the sophistication of Roman artisans. Their ability to create such a complex and beautiful object reflects a society that valued both art and science, blending them seamlessly to produce enduring works of wonder.
The Artistic and Cultural Impact of the Lycurgus Cup
The Lycurgus Cup, beyond its technological marvel, is also a profound artistic and cultural artifact that offers a window into the rich tapestry of Roman society. Its intricate design and mythological narrative not only display the artistic prowess of Roman craftsmen but also reflect the cultural and religious beliefs of the time.
Mythological Significance
Central to the Lycurgus Cup is its depiction of King Lycurgus entangled in vines. According to Greek mythology, Lycurgus was a Thracian king who attempted to thwart the worship of Dionysus, the god of wine. In retaliation, Dionysus drove Lycurgus mad, causing him to attack his own people and eventually meet a gruesome end entangled in vines, symbolic of the god’s power. This mythological scene is rendered with exquisite detail on the cup, showcasing the Romans’ ability to blend narrative and artistry.
This choice of mythological subject matter underscores the cultural significance of Dionysian worship in ancient Rome. The myth of Lycurgus served as a cautionary tale about the dangers of opposing divine will, particularly that of the gods associated with vital aspects of Roman life, such as wine and festivity.
Cultural Context and Usage
The Lycurgus Cup was likely used in ceremonial contexts, possibly related to Dionysian rites. Its ability to change color would have added a magical or divine element to these ceremonies, enhancing the cup’s role as more than just a drinking vessel. This interplay between functionality and symbolism highlights the multifaceted nature of Roman artifacts, where objects often served both practical and spiritual purposes.

The craftsmanship of the Lycurgus Cup also speaks to the status and wealth of its owner. Such a sophisticated and unique piece would have been a luxury item, possibly owned by a high-ranking official or a wealthy patron. Its presence at social or religious gatherings would have signified the owner’s refined taste and deep connection to cultural traditions.
Artistic Techniques and Innovations
The artistic techniques used to create the Lycurgus Cup demonstrate the high level of skill possessed by Roman artisans. The detailed carving required precision and an intimate understanding of both the material and the narrative being depicted. Each figure and element on the cup is rendered with a lifelike quality that brings the myth to vivid life.
Moreover, the integration of nanotechnology within the artistic design suggests a seamless collaboration between artists and craftsmen. This interdisciplinary approach allowed for the creation of an artifact that was not only beautiful but also technologically advanced. The Lycurgus Cup thus stands as a testament to the holistic nature of Roman artistry, where innovation and aesthetics were inextricably linked.
Influence on Later Art and Craftsmanship
The influence of the Lycurgus Cup extended beyond its immediate cultural context. Its discovery and subsequent study have inspired modern artists and scientists alike, showcasing the enduring legacy of Roman innovation. The cup’s ability to captivate both ancient and contemporary audiences highlights the timeless appeal of masterful craftsmanship and the universal fascination with technological marvels.
In the broader scope of art history, the Lycurgus Cup represents a pinnacle of Roman glassmaking and an early exploration of the interplay between light, color, and material. It reminds us that the pursuit of beauty and knowledge often goes hand in hand, driving human creativity to new heights.
The Modern Analysis and Scientific Studies of the Lycurgus Cup
The Lycurgus Cup, with its captivating dichroic properties, intrigued scholars and scientists alike upon its rediscovery in the 19th century. However, it wasn’t until the advent of modern scientific techniques in the 20th century that the true nature of this ancient artifact could be fully understood. The investigation into the Lycurgus Cup has since become a fascinating journey through the realms of art, science, and technology.
Initial Observations and Early Hypotheses
In the early stages of its study, the Lycurgus Cup baffled researchers with its ability to change color under different lighting conditions. Initially, hypotheses were formulated based on the visible characteristics of the glass. Some speculated that the effect was due to the thickness of the glass or the type of pigments used. However, these early theories could not fully explain the dramatic color shift from green to red.
Breakthroughs with Electron Microscopy
The significant breakthrough came with the use of electron microscopy in the mid-20th century. Scientists were able to analyze the glass at a microscopic level, revealing the presence of nanoparticles of gold and silver. These particles, measuring around 70 nanometers, are dispersed within the glass matrix in such a way that they interact with light in a phenomenon known as plasmon resonance.
Plasmon resonance occurs when the electrons in the nanoparticles oscillate in response to specific wavelengths of light. This interaction results in the absorption and scattering of light, causing the glass to appear green when lit from the front and red when backlit. This discovery marked the Lycurgus Cup as an early example of nanotechnology, centuries before the term and concept were formally recognized.
Further Scientific Investigations
Following this discovery, further scientific investigations were conducted to understand the precise methods the Romans used to create such an advanced material. Studies involving spectroscopy, a technique used to measure the interaction of light with matter, provided additional insights into the composition and structure of the glass.
Researchers found that the nanoparticles were not merely a result of accidental contamination but were deliberately incorporated into the glass. This indicated a sophisticated level of knowledge and control over the materials and processes. The Romans had effectively mastered the manipulation of materials at a nanoscale, achieving effects that modern science only began to understand in the late 20th century.
Implications and Applications
The analysis of the Lycurgus Cup has had significant implications for both historical scholarship and modern technology. For historians and archaeologists, it provides a deeper understanding of Roman technological capabilities and artistic practices. It challenges the notion that ancient societies were technologically primitive, showcasing their ability to achieve remarkable feats of engineering and science.
For modern scientists and engineers, the principles observed in the Lycurgus Cup have inspired contemporary applications. The study of plasmon resonance and nanoparticle interactions has influenced fields such as materials science, optics, and nanotechnology. By examining how ancient artisans achieved these effects, researchers have gained insights that could inform the development of new materials and technologies.
The ongoing scientific studies of the Lycurgus Cup continue to reveal new facets of this enigmatic artifact, demonstrating the enduring legacy of Roman innovation and the timeless quest for knowledge and mastery over the natural world.
The Legacy and Influence of the Lycurgus Cup
The Lycurgus Cup, beyond its immediate historical and artistic significance, has left a lasting legacy that continues to influence both modern science and art. Its journey from a ceremonial object in ancient Rome to a subject of modern scientific inquiry reflects the enduring impact of this extraordinary artifact.
Rediscovery and Its Impact on Art and Science
The rediscovery of the Lycurgus Cup in the 19th century marked the beginning of its influence on contemporary art and science. As scholars and artists became aware of its unique properties, the cup inspired a renewed interest in ancient techniques and materials. The ability of the cup to change color under different lighting conditions fascinated not only historians but also glassmakers and artists looking to replicate such effects in their own work.
Modern artists and craftsmen have drawn inspiration from the Lycurgus Cup, experimenting with dichroic glass and other materials to create pieces that play with light and color in similar ways. The cup’s intricate design and technological sophistication have become benchmarks for excellence in glass art, challenging contemporary artists to push the boundaries of their craft.
Scientific Research and Technological Advancements
In the realm of science, the Lycurgus Cup has played a pivotal role in advancing our understanding of nanotechnology and material science. The discovery of nanoparticles in the cup provided a historical precedent for the study of plasmon resonance and its applications.
Researchers have utilized the principles observed in the Lycurgus Cup to develop new technologies in various fields, including optics, photonics, and biomedical engineering. At Mystery Uncover, we delve into the depths of history to bring you fascinating stories of ancient technologies, like the enigmatic Antikythera Mechanism, a device that has puzzled scientists and historians for decades.

For instance, the study of plasmon resonance has led to advancements in medical diagnostics and treatments. Techniques such as surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS), which rely on the same principles that give the Lycurgus Cup its color-changing properties, are now used to detect and analyze biomolecules with high sensitivity. This connection between ancient craftsmanship and modern technology underscores the timeless relevance of the Lycurgus Cup.
Educational and Cultural Significance
The Lycurgus Cup also holds significant educational value. Museums and educational institutions around the world use it as a tool to teach about the intersection of art and science in ancient civilizations. Exhibitions featuring the cup often include interactive displays and detailed explanations of its construction, providing visitors with a deeper appreciation for the technological achievements of the past.
In addition to its scientific and educational contributions, the Lycurgus Cup has become a cultural icon. It symbolizes the ingenuity and creativity of the Roman artisans who crafted it, serving as a reminder of the rich cultural heritage that continues to inspire and inform our modern world. The cup’s enduring appeal lies in its ability to bridge the gap between ancient and contemporary knowledge, highlighting the continuous thread of human innovation.
Modern-Day Value and Preservation
The monetary value of the Lycurgus Cup has also increased significantly due to its historical importance and unique properties. As one of the finest examples of Roman glasswork, it is considered priceless by museums and collectors alike. Efforts to preserve the cup have included advanced conservation techniques to protect its delicate structure and ensure that future generations can continue to study and admire it.
The Lycurgus Cup’s journey from a mysterious artifact to a celebrated example of ancient technology demonstrates its profound impact on multiple fields. Its legacy continues to inspire new generations of artists, scientists, and historians, proving that the wonders of the past still hold valuable lessons for the future.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the Lycurgus Cup?
The Lycurgus Cup is an ancient Roman glass cup from the 4th century AD, famous for its color-changing properties due to the presence of nanoparticles. It depicts the myth of King Lycurgus entangled in vines.
2. How was the Lycurgus Cup made?
The Lycurgus Cup was crafted using dichroic glass, which contains nanoparticles of gold and silver. These particles create different colors depending on the lighting, showcasing early Roman nanotechnology.
3. What is the value of the Lycurgus Cup?
The Lycurgus Cup is considered priceless due to its historical, artistic, and technological significance. Its unique properties and craftsmanship make it an invaluable artifact.
4. Where is the Lycurgus Cup located?
The Lycurgus Cup is currently housed in the British Museum in London, where it is on display for the public to view.
5. What was the Lycurgus Cup used for?
The Lycurgus Cup was likely used in ceremonial contexts, possibly related to Dionysian rites, due to its intricate design and color-changing properties that added a magical element to such ceremonies.
Use of Our Content
⚠️ Content on “Mystery Uncover” is protected under US and International Copyright Laws.
You are free to reuse, republish, and share our content by giving credit to the source as Mystery Uncover with a link to the original material on mysteryuncover.com.






