The Dead Sea, a captivating blend of beauty and intrigue, beckons travelers with its turquoise waters and stark landscapes. But unlike other seas teeming with life, the Dead Sea earns its name for a reason. Ever wondered why is it called the Dead Sea? The answer lies in its unique history, shaped by millions of years of geological transformation and relentless sunshine.
Prepare to be surprised! This seemingly lifeless sea holds a wealth of secrets waiting to be unraveled. In this article we delve into the science behind the Dead Sea’s exceptional saltiness, explore the tenacious life forms that thrive there, and uncover the ongoing discoveries that challenge our understanding of this remarkable place.
A Sea of Salt: Unveiling the Dead Sea’s Hypersaline History
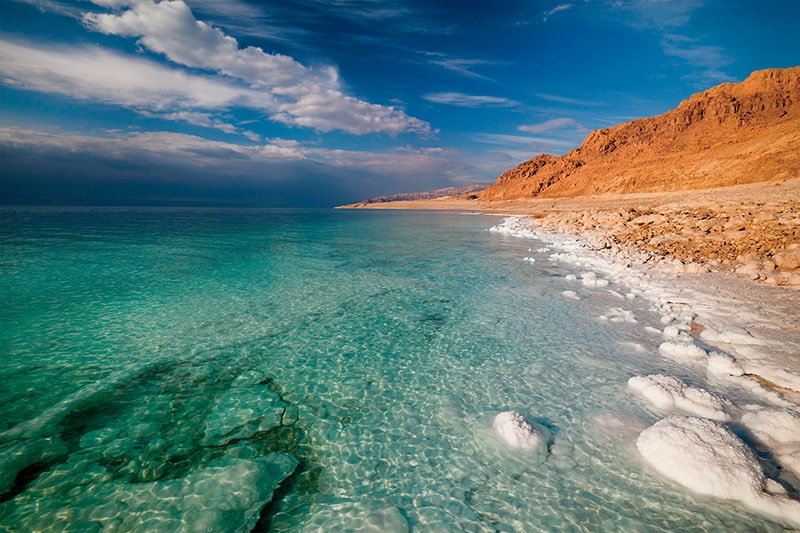
Imagine a vast body of water nestled between Jordan and Israel, its surface shimmering under the desert sun. This is the Dead Sea, a place of stark beauty and intriguing contradictions. Unlike most seas teeming with life, the Dead Sea is eerily silent. No fish dart through its turquoise waters, and no water lilies grace its shores. So, why is it called the Dead Sea? The answer lies in its unique history, a story sculpted by millions of years of geological transformation and relentless sunshine.
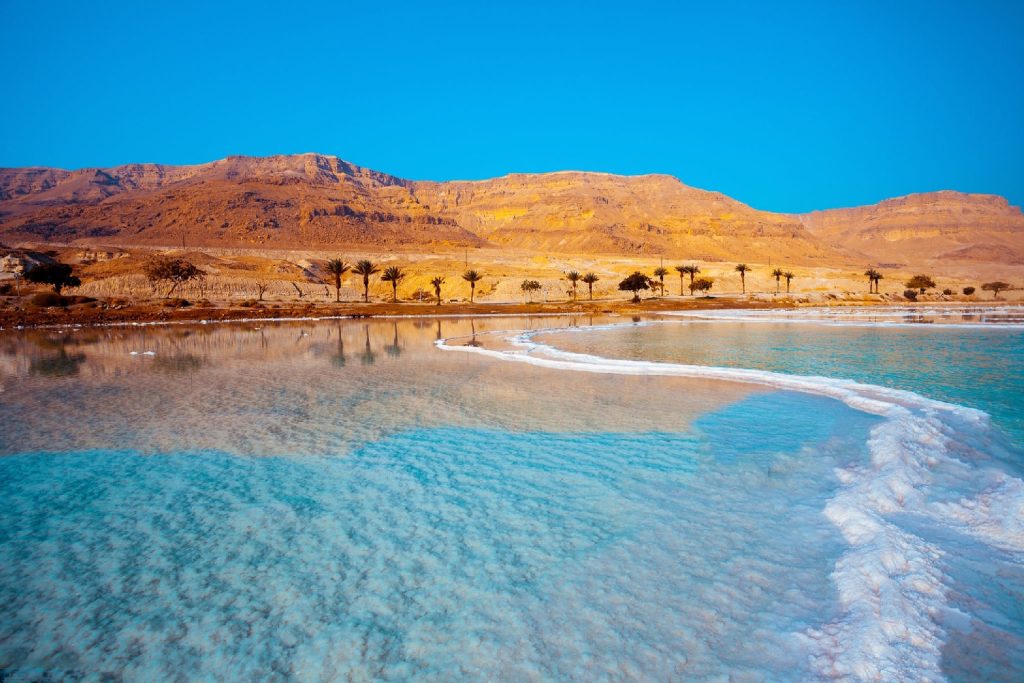

The Dead Sea occupies the lowest point on Earth, a staggering 1,400 feet (430 meters) below sea level. It’s a landlocked lake fed primarily by the Jordan River. However, the story doesn’t end there. The Dead Sea has no outlet, meaning water can only escape through evaporation. Under the scorching desert sun, this evaporation process intensifies. Water molecules escape, leaving behind a concentrated brine – a salty soup that’s about 8 times saltier than the ocean. This extreme salinity, reaching up to 34%, is the very reason why is it called the Dead Sea.
This hypersaline environment is simply inhospitable to most forms of life. The high salt concentration disrupts the internal processes of organisms, making it difficult for them to survive. However, recent discoveries have revealed the presence of some extremophiles – microbes that thrive in harsh environments. These tiny organisms, known as extremophiles have adapted to the Dead Sea’s salinity, showcasing the tenacity of life even in the most unlikely places.
The Dead Sea’s unique history and extreme environment continue to captivate scientists and travelers alike. While it may be devoid of familiar aquatic life, the Dead Sea’s story is far from over. Ongoing research explores the impact of climate change on the Dead Sea’s water levels and salinity, while the search for new extremophiles sheds light on the adaptability of life on Earth. The Dead Sea may be aptly named, but its salty depths hold a wealth of secrets waiting to be unveiled.
Why is it Called the Dead Sea?: Tracing the Evolution of a Name
Long before tourists flocked to the Dead Sea for its buoyant waters and therapeutic mud, civilizations around it have marveled at its unique characteristics. The Dead Sea’s history stretches back millennia, and its names throughout time offer fascinating clues to its exceptional why is it called the Dead Sea question.

One of the earliest names for the Dead Sea, used by the Hebrews around the 2nd millennium BCE, was “Yam HaMelakh” (ים המלח), which translates to “Salt Sea.” This straightforward moniker directly references the sea’s high salt concentration, a characteristic that would become a defining feature throughout history. Another early name, “Lacus Asphaltites” used by the Romans, translates to “Lake of Asphalt.” This name likely stemmed from the naturally occurring bitumen that rises to the surface of the Dead Sea, a byproduct of the decomposition of organic matter in the absence of oxygen (due to the lack of most life forms).
Why is it called the Dead Sea? As various cultures interacted with the Dead Sea, other names emerged. The Arabs referred to it as “Al-Bahr Al-Mayyit” (البحر الميت), meaning “The Dead Sea,” a moniker that reflects the same lifelessness that our modern term captures. Interestingly, some biblical references use “Sea of Sodom” in connection with the Dead Sea, possibly linking its barrenness to the biblical story of Sodom and Gomorrah.
The current name, “Dead Sea,” is a direct translation of the Arabic moniker and perfectly encapsulates the sea’s most striking feature – its inhospitable environment for most aquatic life. The extreme salinity creates an environment where most organisms struggle to survive. Why is it called the Dead Sea? While the term “dead” might seem dramatic, it accurately reflects the stark contrast between the Dead Sea and most other bodies of water teeming with life.
The Dead Sea’s historical names paint a vivid picture of how different cultures have grappled with understanding this unusual natural wonder. Each name, in its own way, sheds light on the sea’s defining characteristic – its exceptional saltiness – which ultimately explains why is it called the Dead Sea.
The Lethal Levels: Understanding the Dead Sea’s Brutal Salt Concentration
The Dead Sea’s lifelessness isn’t a curse or a biblical consequence; it’s a direct result of its incredibly high salt concentration. But what exactly causes this why is it called the Dead Sea situation? Buckle up, because the answer lies in a fascinating interplay between geology, hydrology, and the relentless desert sun.
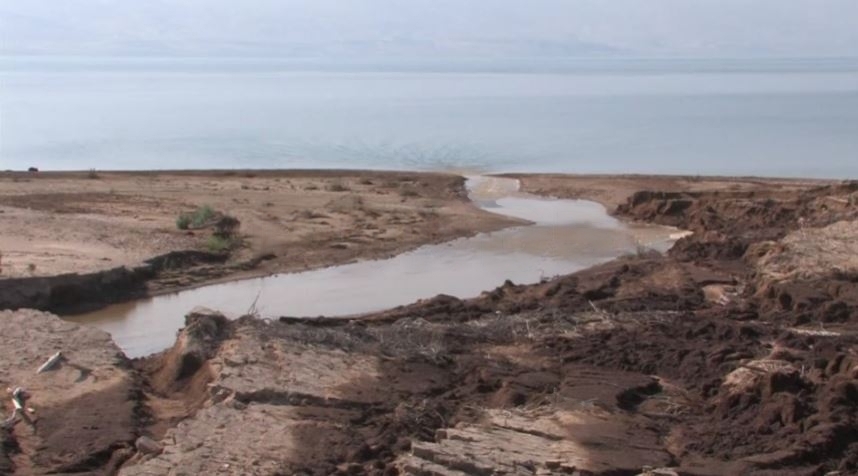

The Dead Sea occupies a closed basin, meaning it has no outlet to the ocean. Its primary source of freshwater is the Jordan River, which snakes its way south from the Sea of Galilee, depositing its precious cargo into the Dead Sea. However, the story doesn’t end there. Unlike other bodies of water with outlets, the Dead Sea can only lose water through evaporation. Imagine a giant pot of saltwater constantly simmering under the scorching desert sun. Water molecules escape as vapor, leaving behind a concentrated brine – a salty soup that gets stronger with each passing day.
Why is it called the Dead Sea? Here’s where things get interesting. Unlike table salt (sodium chloride), which readily dissolves in water, the Dead Sea contains a variety of dissolved minerals, including magnesium, calcium, and potassium chlorides. As water evaporates, these minerals become increasingly concentrated, reaching a staggering 34% salinity – that’s about eight times saltier than the ocean!
This extreme saltiness creates a lethal environment for most living things. The high salt concentration disrupts the internal balance of organisms, essentially dehydrating them from the inside out. Imagine a fish swimming in the Dead Sea; its body constantly tries to maintain a balance of water and salt. With the surrounding water being so salty, the fish’s cells lose water in an attempt to reach equilibrium, ultimately leading to cell death. This harsh reality is the reason the Dead Sea earned its moniker – it’s simply too salty for most life forms to survive.
However, the Dead Sea’s story isn’t entirely devoid of life. Recent discoveries have revealed the presence of extremophiles – microbes that have adapted to thrive in these harsh environments. These tiny organisms showcase the remarkable tenacity of life and its ability to adapt to even the most challenging conditions.
The Dead Sea’s unique geography and relentless sunshine have created a hypersaline environment unlike any other on Earth. Understanding the science behind its why is it called the Dead Sea question not only sheds light on its unique ecosystem but also serves as a stark reminder of the delicate balance between water, salt, and life on our planet.
Life in the Dead Sea? Exploring the Limits of Existence
Why is it called the Dead Sea? The Dead Sea’s nickname paints a clear picture: devoid of life, a desolate aquatic graveyard. While the vast majority of complex organisms struggle to survive in its hypersaline environment, recent discoveries have thrown a surprising twist into the narrative. So, is there any life in the Dead Sea? The answer, defying the expectations of a why is it called the Dead Sea question, is a resounding yes, albeit with a fascinating caveat.
While fish, seaweed, and other familiar aquatic life are conspicuously absent, the Dead Sea isn’t entirely devoid of living organisms. Scientists have discovered a surprising array of microbes – single-celled bacteria and archaea – thriving in this harsh environment. These extremophiles, as they’re aptly called, have evolved remarkable adaptations to survive the Dead Sea’s brutal salinity.
One such adaptation involves the use of compatible solutes. Imagine these microbes as tiny ships navigating a hyper-saline sea. To maintain their internal pressure and prevent dehydration, they accumulate special molecules that can balance the high concentration of salt outside their cells. It’s a clever strategy that allows them to exist in an environment that would be lethal to most other life forms.
Why is it called the Dead Sea? The presence of these extremophiles challenges the notion of the Dead Sea being entirely “dead.” It showcases the incredible resilience of life and its ability to adapt to even the most extreme conditions. These microbes not only survive but also find ways to thrive in a hypersaline environment that would spell doom for most creatures.
However, it’s important to remember that the Dead Sea’s microbial life is vastly different from the teeming ecosystems found in most oceans and lakes. The Dead Sea lacks the complex food webs and biodiversity that characterize healthy aquatic environments. Why is it called the Dead Sea? While the presence of extremophiles adds a fascinating layer to the Dead Sea’s story, it doesn’t negate the fact that the vast majority of life struggles to survive in its harsh waters.
The discovery of microbial life in the Dead Sea raises intriguing questions. Why is it called the Dead Sea? What other extremophiles might lurk beneath the surface? How have these organisms adapted to survive in such a challenging environment? Further research into the Dead Sea’s microbial communities could not only shed light on the limits of life on Earth but also provide valuable insights into the potential existence of life on other planets with extreme environments.
The Dead Sea may be aptly named for its inhospitable environment for most life forms, but the presence of these tenacious microbes adds a surprising twist to the story. It’s a testament to the remarkable adaptability of life and a reminder that even in the harshest environments, life finds a way.
Beyond the Name: The Ecological and Geological Impact of the Dead Sea
The Dead Sea’s moniker may be a stark reminder of its inhospitable environment for most aquatic life, but its significance extends far beyond the question of why is it called the Dead Sea. This unique body of water plays a critical role in the region’s ecology and geology, shaping the landscape and supporting a surprisingly diverse ecosystem.

Ecologically, the Dead Sea acts as a natural filter, trapping pollutants and minerals carried by the Jordan River. While this filtration process helps maintain the quality of water downstream, the Dead Sea itself faces ecological challenges. The ever-increasing salinity and shrinking water levels threaten the delicate balance of its microbial ecosystem. Conservation efforts are underway to address these issues and ensure the Dead Sea’s continued ecological role.
Why is it called the Dead Sea? Geologically, the Dead Sea sits in a fascinating tectonic depression, the Dead Sea Transform. This active fault zone is responsible for the ongoing movement of the Arabian Plate away from the African Plate. The Dead Sea’s basin continues to deepen as the plates diverge, creating a unique geological environment where geothermal activity and mineral-rich brines play a significant role. Studying the Dead Sea’s geological formations provides valuable insights into the Earth’s crustal movements and the ongoing process of continental drift.
The Dead Sea’s mineral-rich waters and mud have also been prized for their therapeutic properties for centuries. People flock to the Dead Sea shores to bathe in its buoyant waters and slather themselves in the mineral-rich mud, believed to alleviate various skin conditions. The Dead Sea’s unique composition has also fueled economic activity through the extraction of minerals like potash and bromine, used in fertilizers and industrial applications.
Nature’s Mystery: How Were the Chocolate Hills Formed?
Have you ever wondered about the origin of the mysterious Chocolate Hills in the Philippines? These dome-shaped hills, numbering in the thousands, blanket a vast landscape and have captivated geologists for decades. To explore the various theories about their formation, check out our article How Were the Chocolate Hills Formed?
In conclusion, the Dead Sea’s significance goes far beyond the explanation for why is it called the Dead Sea. It’s a dynamic ecosystem, a geological marvel, and a source of economic and therapeutic value. Understanding the Dead Sea’s multifaceted nature allows us to appreciate its importance and the need for its conservation. As research continues, the Dead Sea’s secrets will continue to unfold, offering valuable insights into the delicate balance of our planet’s ecosystems and the remarkable tenacity of life.
A Place of Intrigue: The Dead Sea’s Future and Ongoing Discoveries
The Dead Sea, aptly named for its lifelessness for most complex organisms, continues to captivate scientists and travelers alike. While the why is it called the Dead Sea question is readily answered by its extreme salinity, the story doesn’t end there. This captivating body of water remains a place of ongoing research and potential future discoveries.

One of the most pressing concerns surrounding the Dead Sea is its rapidly receding water levels. Why is it called the Dead Sea? Climate change and increased water diversion from the Jordan River have significantly impacted the Dead Sea’s volume. Scientists are actively researching ways to mitigate these effects and ensure the long-term sustainability of this unique ecosystem.
Beyond water levels, the Dead Sea’s microbial communities are a hotbed of ongoing research. New extremophile species are constantly being discovered, each with its unique adaptations to the harsh environment. Understanding how these microbes survive and thrive could provide valuable insights into the potential existence of life on other planets with extreme environments.
The Dead Sea’s geological history also holds secrets waiting to be unveiled. Studying the layers of sediment beneath the seabed offers a glimpse into past climates and environmental conditions. These insights can help us understand long-term climatic trends and predict future changes that might impact the Dead Sea and surrounding regions.
The Dead Sea’s future remains uncertain, but one thing is clear: it’s a place of ongoing discoveries. As research continues, we can expect to learn more about the Dead Sea’s unique ecosystem, its role in the region’s geology, and the potential for new life forms thriving beneath its salty surface. The Dead Sea may be aptly named for its lack of familiar aquatic life, but its ongoing story is far from over.
Perhaps future discoveries will even challenge the notion of “dead” altogether. The Dead Sea may surprise us yet again, proving that even in the harshest environments, the potential for life and new discoveries is ever-present. So, the next time you ponder why is it called the Dead Sea, remember that this captivating place holds a wealth of secrets waiting to be unraveled.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Why is the Dead Sea called the Dead Sea?
The Dead Sea gets its name from its extremely high salt concentration, which makes it inhospitable for most aquatic life. With a salinity of around 34%, the Dead Sea is about eight times saltier than the ocean. This harsh environment disrupts the internal balance of organisms, essentially dehydrating them from the inside out. While recent discoveries have revealed the presence of some extremophiles (microbes that thrive in harsh environments), the Dead Sea remains largely devoid of familiar aquatic life, earning its moniker.
2. Does anything live in the Dead Sea?
Surprisingly, yes! While fish, seaweed, and other familiar aquatic life are absent, the Dead Sea is home to a surprising array of microbes – single-celled bacteria and archaea. These extremophiles have adapted to the Dead Sea’s brutal salinity through clever strategies like using compatible solutes to maintain their internal pressure and prevent dehydration. The presence of these microbes challenges the notion of the Dead Sea being entirely “dead” and showcases the remarkable adaptability of life.
3. What is the Dead Sea’s significance beyond its name?
The Dead Sea plays a critical role in the region’s ecology and geology. It acts as a natural filter for the Jordan River, trapping pollutants and minerals. Geologically, the Dead Sea sits in a fascinating tectonic depression, the Dead Sea Transform, providing insights into crustal movements and continental drift. The Dead Sea’s mineral-rich waters and mud have also been prized for their therapeutic properties for centuries and are a source of economic activity through the extraction of minerals.
4. What are some of the challenges facing the Dead Sea?
The Dead Sea faces several challenges, including rapidly receding water levels due to climate change and increased water diversion. Scientists are actively researching ways to mitigate these effects and ensure the long-term sustainability of this unique ecosystem.
5. What does the future hold for the Dead Sea?
The Dead Sea’s future remains uncertain. However, ongoing research holds promise for new discoveries. Scientists are exploring the Dead Sea’s microbial communities, its geological history, and the potential for new life forms. The Dead Sea may surprise us yet again, proving that even in the harshest environments, the potential for life and new discoveries is ever-present.
Use of Our Content
⚠️ Content on “Mystery Uncover” is protected under US and International Copyright Laws.
You are free to reuse, republish, and share our content by giving credit to the source as Mystery Uncover with a link to the original material on mysteryuncover.com.





