In the shadow of Egypt’s towering pyramids lies a lesser-known marvel—Ancient Egyptian locks. These intricate devices, crafted over 4,000 years ago, were not just tools of security but symbols of power and protection. Imagine a world where the safety of sacred temples, royal tombs, and priceless treasures depended on the genius of early locksmiths. As we unravel the secrets behind these locks, you’ll discover how they shaped the very concept of security and left an indelible mark on civilizations to come. Dive into the fascinating world of Ancient Egyptian locks and unlock their mysteries.
The Ingenious Locks of Ancient Egypt
In the vast annals of history, ancient Egypt shines as a civilization of unparalleled innovation. Amid the grandeur of pyramids and the enigma of hieroglyphs, there lies a lesser-known marvel: the intricate and sophisticated world of Ancient Egyptian locks. These locks, some of the earliest known to humanity, were not merely functional; they were a testament to the Egyptians’ profound understanding of security and craftsmanship.
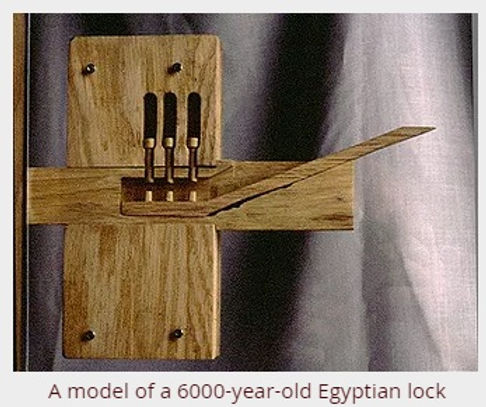

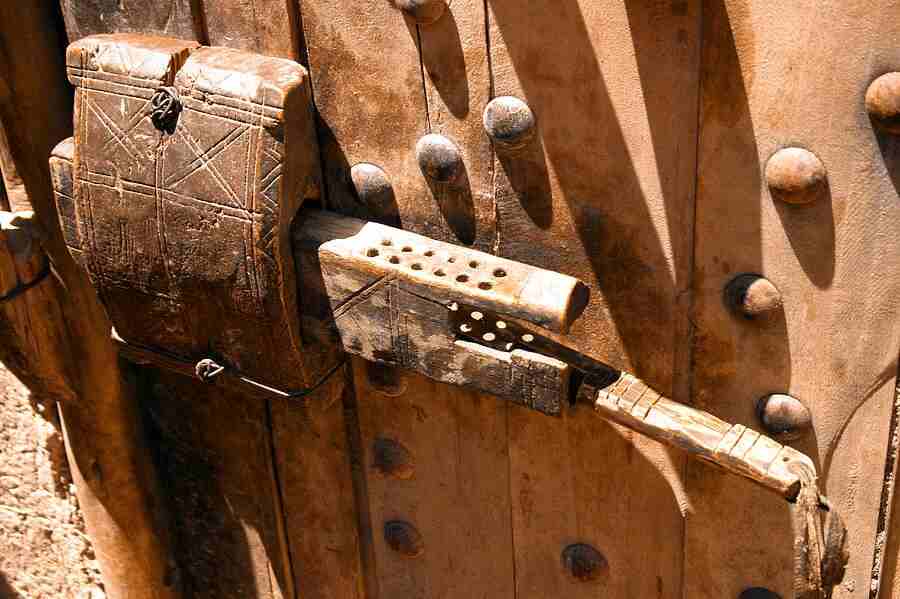
The journey of Ancient Egyptian locks begins around 2000 BCE, during the Middle Kingdom period. This era marked a significant evolution in the way Egyptians approached security. Prior to this, rudimentary mechanisms, likely made of simple wood or stone, were used to safeguard property. However, the Middle Kingdom saw the advent of more complex wooden locks, which featured an early form of pin tumbler technology. This innovation was revolutionary, representing a leap from basic fastening systems to mechanisms that required a precise interaction between lock and key.
These early locks were constructed primarily from wood, a material both abundant and malleable. The design was straightforward yet ingenious: a wooden bolt would slide into place, secured by a series of movable pins. The corresponding key, often made from the same material, had protrusions that matched the configuration of the pins. When inserted, the key lifted the pins, allowing the bolt to retract and the lock to open. This system, though primitive by modern standards, was a remarkable achievement for its time.
The use of Ancient Egyptian locks wasn’t limited to practical purposes alone. They were also symbolic, reflecting the Egyptians’ deep belief in protection, not just of physical assets but also of the spiritual sanctity of sacred spaces. Temples, tombs, and storerooms—all were guarded by these early security devices, highlighting the Egyptians’ understanding of the need for both physical and metaphysical security.
The Birth and Evolution of Locks in Ancient Egypt
As we delve deeper into the timeline of Ancient Egyptian locks, it becomes clear that their evolution was not merely a result of technical ingenuity but also a response to the growing complexities of Egyptian society. During the New Kingdom period, roughly 1550 to 1070 BCE, Egypt reached the zenith of its power and wealth. With this prosperity came an increased need for security, particularly in safeguarding the ever-expanding troves of valuables, sacred texts, and treasures housed within temples and royal tombs.
The locks of this era reflected the Egyptians’ advanced understanding of mechanics and their ability to adapt to the changing demands of their time. By now, the simple wooden locks of the Middle Kingdom had evolved into more sophisticated devices. These Ancient Egyptian locks featured intricate mechanisms made of wood and sometimes bronze, a material that was harder and more durable. The use of bronze represented a significant advancement, allowing for more intricate designs and greater resistance to tampering.

The craftsmanship of these locks was extraordinary. The lock’s internal structure often involved multiple pins or tumblers, each meticulously crafted to fit a specific key. These keys, often carved from wood or cast in bronze, were unique to each lock, ensuring that only the correct key could trigger the mechanism. This development was crucial for securing important structures and was a clear indication of the Egyptians’ forward-thinking approach to security.
Furthermore, these Ancient Egyptian locks were often decorated with symbols and inscriptions, adding layers of meaning beyond their practical use. Such embellishments were not merely decorative; they were imbued with protective charms and invocations to the gods, reflecting the deep connection between physical security and spiritual protection in ancient Egyptian culture. This dual purpose—securing the physical and invoking the divine—underscored the significance of these locks in the daily and spiritual lives of the Egyptians.
Design and Construction: Craftsmanship of Ancient Egyptian Locks
The design and construction of Ancient Egyptian locks reveal not only the Egyptians’ technical prowess but also their deep appreciation for artistry. As these locks evolved over time, so too did the complexity of their mechanisms and the craftsmanship involved in their creation. What began as simple wooden bolts developed into sophisticated security devices that demonstrated a remarkable understanding of mechanics and material science.
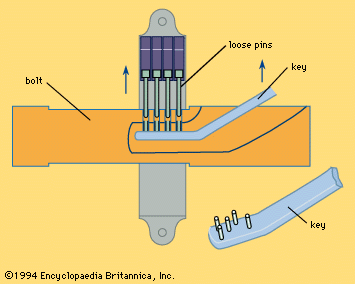
The typical Ancient Egyptian lock was composed of two main components: the lock mechanism itself and the key. The lock, often crafted from wood or bronze, was a rectangular or cylindrical device attached to a door or chest. Inside the lock, a series of pins or tumblers were set into place. These pins needed to be lifted to a precise height in order for the bolt to slide and the lock to open.
This early form of the pin tumbler mechanism, later refined in different cultures, was a critical innovation in lock-making. The key, usually made from wood but occasionally from bronze, was a long, flat piece with protrusions or teeth that matched the internal configuration of the lock. When inserted, the key would align the pins, allowing the bolt to move freely.
The ingenuity of these locks lay in their simplicity. While the mechanism itself was straightforward, it was highly effective in preventing unauthorized access. Each lock was custom-made, with the key specifically designed to fit only that particular lock. This ensured that the lock could not be easily picked or tampered with—a crucial feature in a society where safeguarding sacred and valuable objects was of paramount importance.
In addition to their functional role, Ancient Egyptian locks were often adorned with intricate carvings and symbols. These decorations were more than mere ornamentation; they served as protective charms, invoking the power of gods like Anubis, the protector of graves, to guard the contents secured by the lock. This blend of functionality and spirituality made these locks not just tools of security, but symbols of the Egyptians’ broader worldview, where the physical and the metaphysical were closely intertwined.
Symbolism and Security in Ancient Egyptian Society
In ancient Egypt, the significance of Ancient Egyptian locks extended beyond mere physical security; they were deeply intertwined with the spiritual and symbolic dimensions of life. The Egyptians lived in a world where the seen and unseen coexisted, and their locks reflected this dual reality. These devices were not only practical tools but also bearers of symbolic meaning, often adorned with religious motifs and protective symbols that conveyed a deeper sense of purpose.
The Egyptians believed that the act of securing something—whether it was a tomb, a temple, or a chest of valuables—was an act of protection that went beyond the material realm. Ancient Egyptian locks were often engraved with symbols invoking the gods’ protection, such as the Eye of Horus, which symbolized healing and protection, or the Ankh, representing life. These symbols were believed to imbue the locks with spiritual power, acting as a deterrent not only to physical intruders but also to malevolent spiritual forces.

In temples and tombs, where the stakes were highest, these locks took on an even greater significance. The sanctity of these spaces demanded that they be protected from both earthly thieves and supernatural threats. The intricate locks, with their carefully crafted mechanisms and sacred symbols, were seen as essential in maintaining the purity and safety of these hallowed places. To breach a lock guarding a tomb was not only a criminal act but also a profound sacrilege, disturbing the delicate balance between the living and the dead.
Moreover, the symbolic use of Ancient Egyptian locks was not confined to religious contexts. In everyday life, they played a role in safeguarding personal belongings, reinforcing the idea that protection was a universal concern, transcending social class. Whether used by a pharaoh or a commoner, these locks were a testament to the Egyptians’ understanding that security, in all its forms, was a fundamental need deeply rooted in both the physical and spiritual realms.
In the same way that Ancient Egyptian locks reveal the advanced understanding of security in ancient times, other artifacts like the Nimrud Lens challenge our perceptions of ancient technologies. Discovered in the Assyrian city of Nimrud, this lens is believed by some to have been used as a tool for magnification or even as part of an ancient telescope, sparking debates about the technological capabilities of ancient civilizations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are Ancient Egyptian Locks?
Ancient Egyptian locks are some of the earliest known security devices, designed and crafted in Egypt around 2000 BCE. These locks featured a pin tumbler mechanism and were made primarily of wood or bronze, reflecting both practical and symbolic significance in ancient Egyptian society.
2. Who invented Ancient Egyptian Locks?
The invention of Ancient Egyptian locks is credited to the skilled craftsmen of Egypt during the Middle Kingdom period. These artisans developed the pin tumbler lock mechanism, which became a foundational technology for security in subsequent civilizations.
3. How did Ancient Egyptian Locks influence modern security?
Ancient Egyptian locks laid the groundwork for modern lock mechanisms, particularly through their development of the pin tumbler system. This technology was passed down through cultures, eventually evolving into the advanced locks used in contemporary security.
4. What materials were used in Ancient Egyptian Locks?
Ancient Egyptian locks were primarily made from wood, with later versions incorporating bronze for added durability. The use of these materials allowed for both functional and decorative designs, with some locks featuring intricate carvings and symbols.
5. What symbolic meanings did Ancient Egyptian Locks hold?
Ancient Egyptian locks often bore religious symbols, such as the Eye of Horus or the Ankh, believed to provide spiritual protection. These locks served not only as physical security devices but also as talismans to guard against both earthly and supernatural threats.
Legacy and Influence: The Lasting Impact of Ancient Egyptian Locks
The legacy of Ancient Egyptian locks is far-reaching, echoing through the corridors of time to influence the development of security mechanisms across civilizations. As trade routes expanded and cultural exchanges became more frequent, the knowledge and techniques of Egyptian lock-making began to spread beyond the borders of the Nile Valley. This dissemination of technology was not just a transfer of practical knowledge but also a transmission of ideas about security, craftsmanship, and the protection of both material and spiritual wealth.
One of the most significant ways in which Ancient Egyptian locks influenced other cultures was through their mechanical innovation. The concept of the pin tumbler mechanism, which was refined by the Egyptians, laid the groundwork for future developments in lock-making. As this technology traveled along trade routes, it was adapted and modified by other civilizations, each adding their own refinements and innovations. The basic principles, however, remained rooted in the ingenuity of the Egyptians, whose understanding of security was centuries ahead of its time.
The influence of these locks can be seen in ancient Greece and Rome, where similar mechanisms began to appear, albeit with enhancements suited to the needs and materials available in those regions. The Romans, in particular, recognized the value of the pin tumbler system and incorporated it into their own designs, further advancing the technology. This cross-cultural exchange highlights how the Egyptians’ contributions to security technology transcended their own civilization, leaving an indelible mark on the history of locks and keys.
Beyond the mechanical influence, the symbolic use of Ancient Egyptian locks also found resonance in other cultures. The idea that locks could serve both a practical and spiritual function was adopted by other societies, where the protection of sacred spaces and valuables was equally paramount. The Egyptians’ dual approach to security—physical and metaphysical—thus became a model for other civilizations to follow, ensuring that their legacy would endure long after the sands of time had buried their temples and tombs.
Use of Our Content
⚠️ Content on “Mystery Uncover” is protected under US and International Copyright Laws.
You are free to reuse, republish, and share our content by giving credit to the source as Mystery Uncover with a link to the original material on mysteryuncover.com.






